Sub genus : Nannomonas
Trypanosoma congolense
Introduction
- This parasite produces acute and serious type of ‘Nagana’ disease in sheep, goat, cattle, horse and pig.
Location and host
- Found in blood/ plasma of cattle , sheep, goat, horse and pig.
- Glossina spp. Act as arthropod vector
- Reservoir host: Antelope, Giraffe, Zebra, Elephant and Warthog.
Morphology
- Small, mono-morphic in form and measure 8-20 µm.
- Undulating membrane is inconspicuous
- Kinetoplast is of medium-sized and posterior end is blunt
- No free flagellum
- Sluggish type of movement in fresh blood films, often attached to red cells.
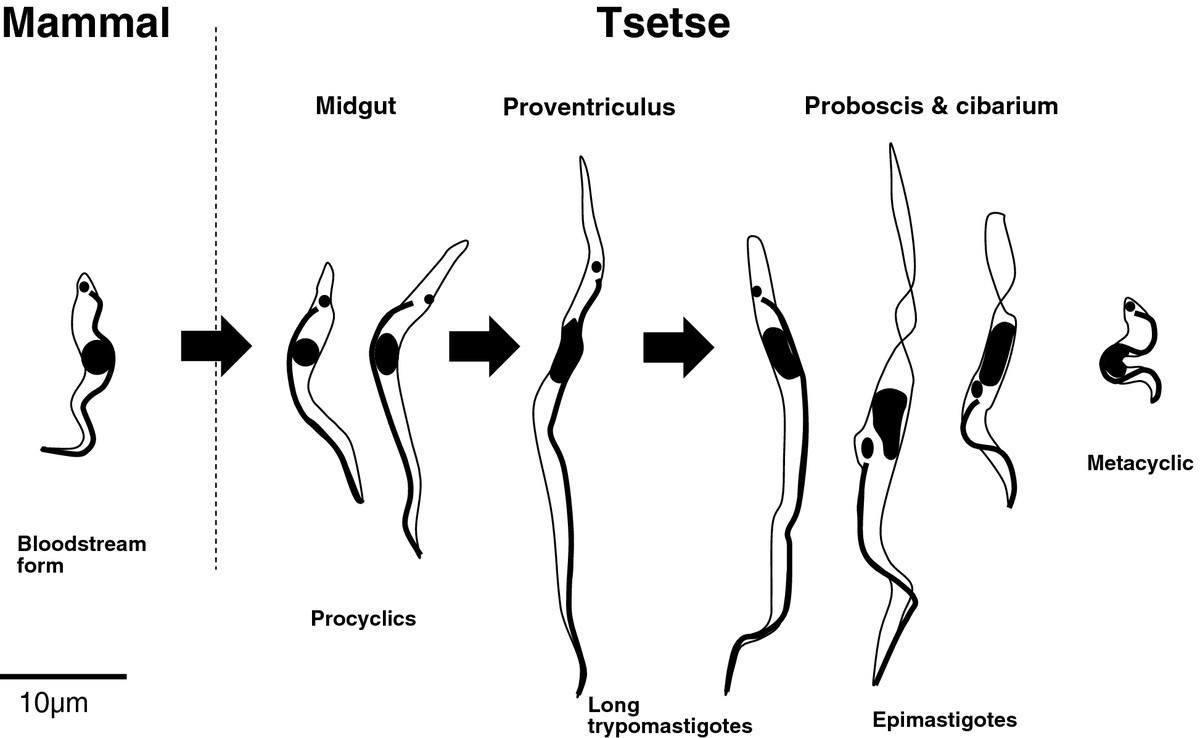
Life cycle
- Host acquire infection when Glossina flies injects infective metacyclic trypomastigote
- After inoculation of metacyclic trypomastigotes, they change into trypomastigote and multiplies by longitudinal binary fission.
- These blood forms of parasites are then taken up by vector. Inside vector, they first develop into mid gut as long tryptomastigote form without free flagellum.
- Then they develop in proboscis where they change into epimastigote form, Epimastigote multiplies there.
- Epimastigote forms change into metacystic trypomastigote forms
- These forms when injected into skin, parasite multiply and migrate via lymph to blood.
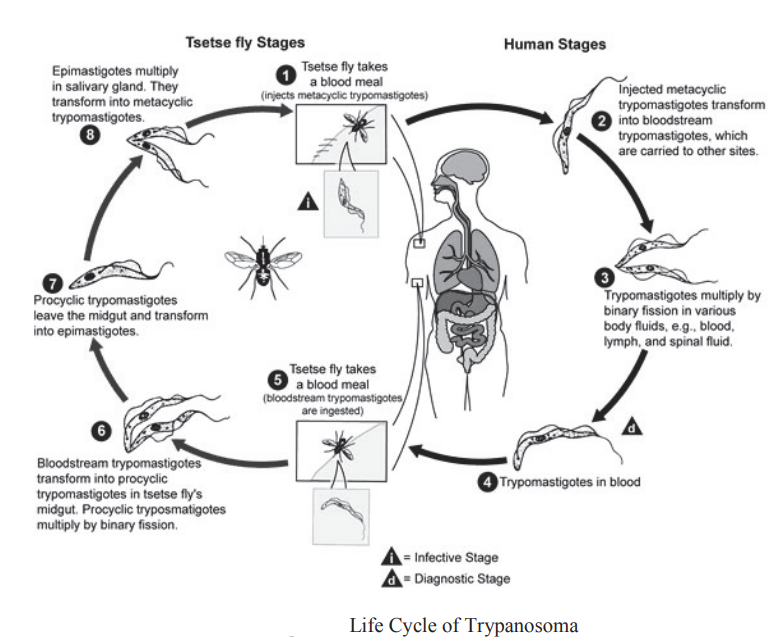
Transmission
- Inoculation of parasite by vector flies
Pathogenesis / Clinical signs
- In cattle, parasite cause acute fatal disease resulting in death in about 10 weeks. It also causes african trypanosomiasis.
- Clinical signs exhibited by animals include : Seere anemia, Irregular fever, Emaciation, Sub-cutaneous edema, Conjunctivitis, Photophobia and Lachrymation
- NO effect in CNS.
Note: Conspicuous: Clearly visible , Inconspicuous : not clearly visible
Diagnosis
- Clinical signs are not pathognomonic but signs provide tentative diagnosis for this case.
- Demonstration of parasite in blood.
Treatment
- Two drugs are common in use: Diminazone aceturate (Berenil) and homidium salts (Ethidium and Novidium)
- Diminazene aceturate (Berenil) @ 3.5 mg/kg body weight , intramuscular and sub cutaneous.
- Ethidium bromide @ 1 mg/kg body weight in cattle
Control
- Use of fly repellants and insecticides
- Control of breeding of insect vectors.