Toxoplasma gondii
Location and Host
- Feline animals and cats are definitive host.
- Any warm-blooded animals including human or birds are intermediate host.
- These parasites are found in intestine of cat, muscle, lung, liver, reproductive system.
Morphology
- Oocyst are round to slightly oval and measure average of 13 µm x 11 µm.
- Sporulated oocyst contain two ellipsoidal sporocysts, each sporocyst further contains four sporozoites.
- Three infectious stages of toxoplasma are found; tachyzoites( in pseudocyst) , bradyzoites (in tissue cyst) and sporozoites ( in oocyst).
- Bradyzoites are slowly dividing forms and tachyzoites are rapidly dividing forms, in cells of definitive host.
- Tachyzoites are found developing in vacuoles in many cell types. Ex: fibroblast, hepatocytes, reticular cells and myocardial cells, 8-15 organism may be present in any one cell.
- Tissue cyst are found in muscle, liver, lung and brain and may contain several thousand lancet-shaped bradyzoites.

Mode of transmission
- Transmission occurs through 3 primary ways.
- Congenital
- Carnivorism
- Faeco-oral route
Lifecycle
- Lifecycle is heteroxenous and occurs in two cycles:
- Enteroepithelial cycle
- Extraintestinal cycle
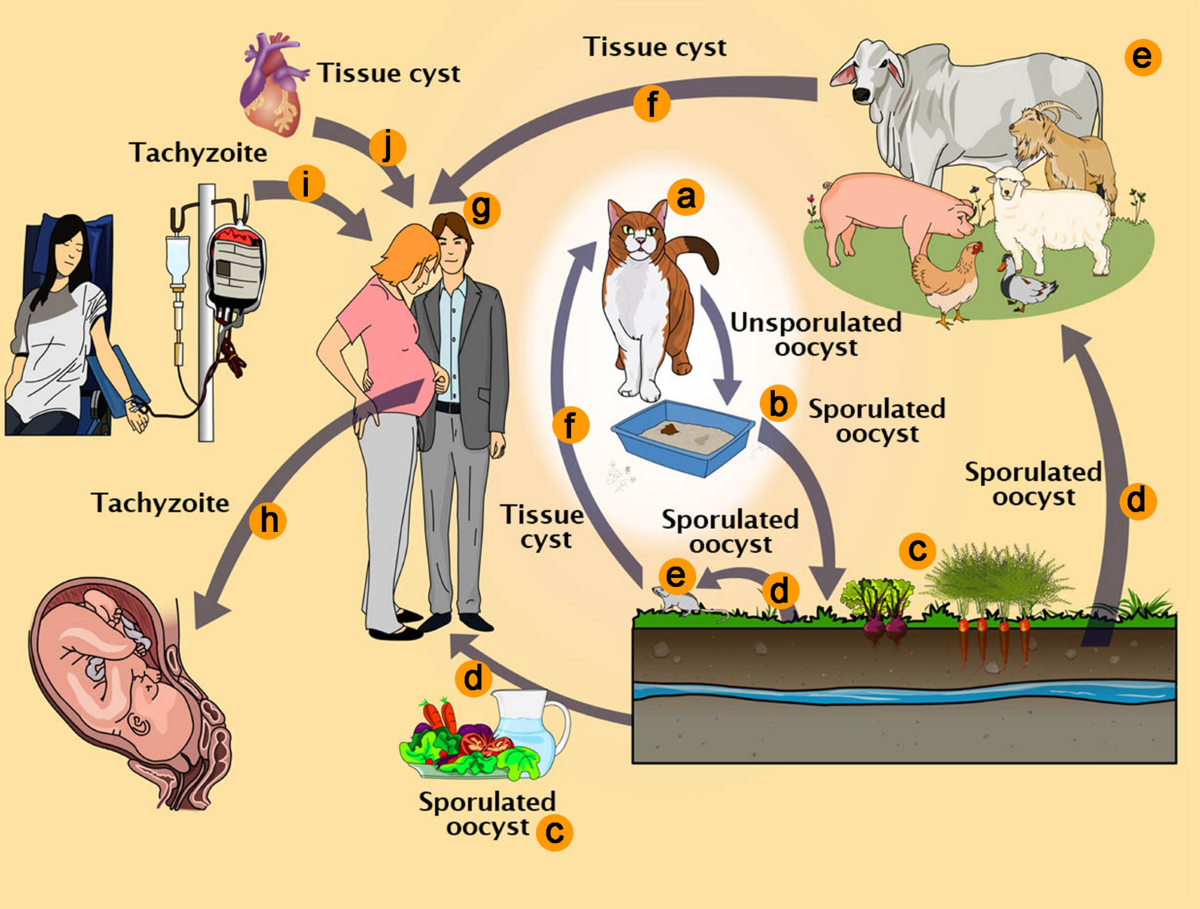
Enteroepithelial cycle
- It takes place in definitive host; cat and other feline species.
- Definitive host gets infection by ingestion of any three infective sages of toxoplasma (bradyzoites, tachyzoites or sporozoites)
- After ingestion of tissue cyst, cyst wall is hydrolyzed by proteolytic enzymes in stomach and small intestine.
- Bradyzoites released penetrates epithelial cell of small intestine. A series of genetically determined asexual generation (Type A-E) occurs followed by sexual cycle.
- Type A is smallest type and appears 12-18 hours after infection. Type A is divided by endodyogeny and changes to type B after 12-34 hours of infection.
- Type B has centrally located nucleus and divides by endodyogeny and endopolygeny and forms type C after 25-34 hours of infection.
- Type C are elongate and have sub-terminal nucleus. Divide by Schizogony and forms type D and occurs from 32 hours-15 days of infection.
- Type D are smaller than type C and divides through endopolygeny, schizogony and produces type E, which occurs 3-15 days after infection.
- Type E are elongate and have sub-terminal nucleus multiplies by schizogony. Merozoites released from type D and type E initiate gamete formation. This occurs in small intestine, throughout ileum, 3-15 days after infection.
- Macrogametes are ovoid to ellipsoidal in shape and few in number. Microgametes, when mature, penetrate macrogametes and oocyst are formed.
- Oocyst are discharged into intestinal lumen by rupture of intestinal epithelial cells when they mature.
- Unsporulated oocyst are discharged through faeces. Sporulation occurs outside host within 1-5 days. Sporulated oocyst are sub-spherical to ellipsoidal.
Note: Sometimes bradyzoites penetrate lamina propria and multiply and tachyzoites within few hours after infection. T. gondii spread to extra-intestinal tissues of cats via lymph and blood. This cycle is similar to that in non-feline host with two exceptions:
- Tachyzoites have not been demonstrated in feline intestinal epithelial cells.
- Type D and E are non-infectious to mice, by any route
Extraintestinal cycle
- It occurs in extra-intestinal tissue of intermediate host. Some time, cat may also act as intermediate host.
- After ingestion of sporulated oocyst, intermediate host gets infection.
- Oocyst ruptures in intestine, releasing 8 sporozoites.
- Sporozoites multiplies intercellularly in intestinal epithelium and associated lymph nodes and tachyzoites are formed.
- They spend to other parts of body through lymph and blood and encyst in brain, skeletal muscle, cardiac muscles and liver.
- On ingestion of infected meat having tissue cyst of gondii, proteolytic enzymes dissolve cyst wall, releasing bradyzoites. After entering host cell, bradyzoites transform into tachyzoites.
- Tachyzoites undergoes repeated division ultimately encysting in tissue. Cycle gets completed when tissue cysts are ingested by cat.
Note: Transplacental infection occurs when previously non-infected host become infected during pregnancy. T. gondii multiplies placenta and then spreads to foetal tissues. Foetus are more severely affected when dam becomes infected during first half gestation.