Reproduction of protozoans
- Reproduction may be asexual or sexual.
- Asexual reproduction may occur for a variable period and follows sexual process.
A. Asexual reproduction
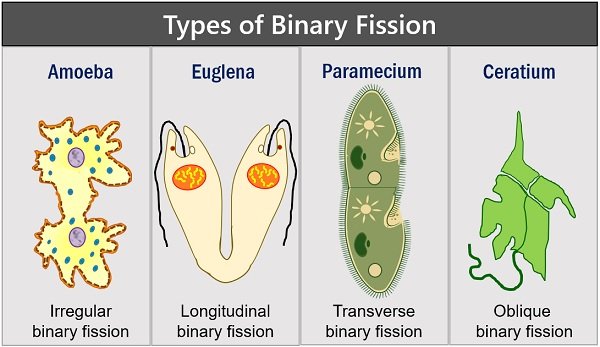
a. Binary fission
- Commonest form of asexual reproduction.
- Asexual division of individual into two parts is called binary fission.
- Division results in two similar halves and each one become independent individual.
- Division either occurs on longitudinal axis of cell body called longitudinal binary fission or on an transverse axis called transverse binary fission.
- Longitudinal binary fission is seen in case of flagellated protozoa (zoo mastigophore class) whereas transverse binary fission is seen in ciliates. However, protozoa having asymmetrical body. Ex: Amoeba undergo binary fission on any plane of the body.
b. Budding
- Asexual reproduction in which small daughter individual separates from mother cell and grows to full size. This is mitotic division.
- Internal budding endodyogeny: Two daughter cells are formed within mother cell and then break out after destroying it. Ex: Protozoa under family sarcocystidae.
- Endopolygeny: More than two daughter cells are formed in the budding.

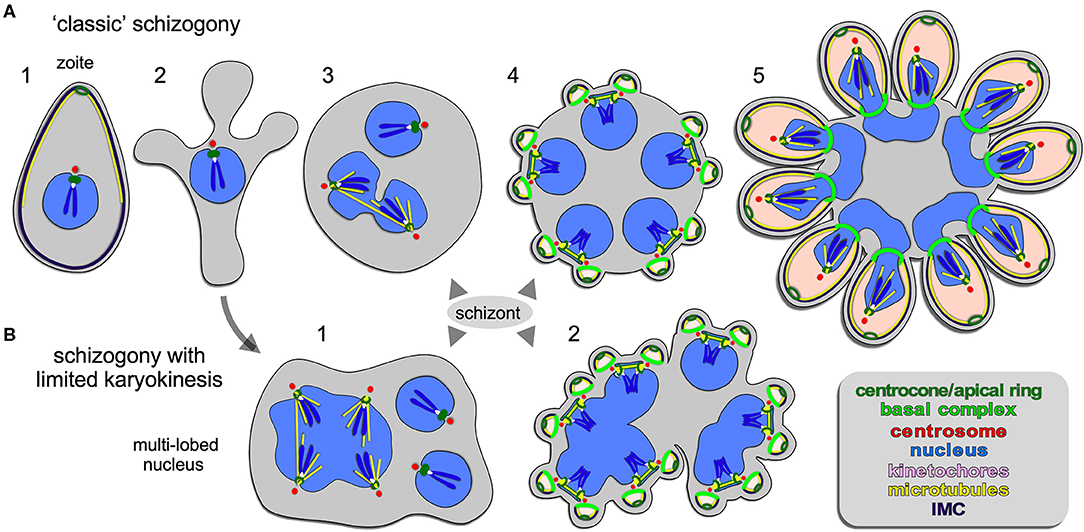
c. Multiple fission / schizogony or merogony
- Nucleus divides mitotically several times before cytoplasm divides.
- Found in phylum Apicomplexa.
- Dividing parasite with a multinucleated mass is called a schizont, agamont, meront or segmenters. Daughter cells are called merozoites or schizoites.
B. Sexual reproduction
- Two types of sexual division occur in protozoa.
a. Syngamy
- Two individual gametes fuse to form a zygote.
- If two gametes are similar in appearance, they are called isogametes and process of their fusion is called isogamy.
- If two gametes are structurally different, they are called anisogametes and process of their fusion is called anisogamy. Smaller gamete is male gamete, also called microgamete and larger one is female gamete and is called macrogamete.
- These gametes are produced from special cells called microgametocytes (microgametes) and macrogametocytes (macrogametes) respectively. Process of gamete formation is called gametogony which follows asexual reproduction by sporogony.
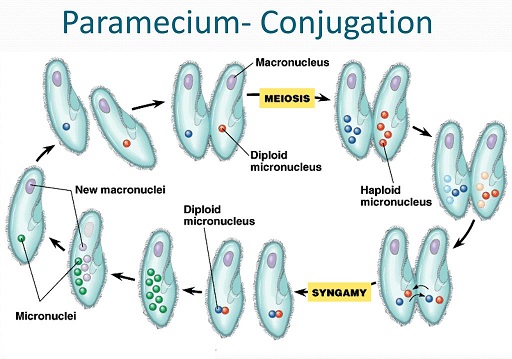
b. Conjugation
- Two individuals come together temporarily and fuse along part of their length.
- Macronucleus in each individual undergoes disintegration and finally disappears. Micronucleus on other hand becomes active and divides a number of times but only one of the resultant haploids pronuclei passes from each conjugant into other and all rest disintegrate and disappear.
- After this exchange of nuclear material from micronucleus, two individual separate and nuclear reorganization occurs.
- Usually found among ciliates.
Note:
- Sporogony usually follows syngamy.
- Zygote may or may not then divide by asexual process of multiple fission to form number of individuals called sporozoites.
- In some protozoa, zygote develops a resistant cystic wall around the whole organism.
- Spore is produced within organism by formation of heavy wall around one or more organism called sporozoites. It is infective stage of protozoan which may occur outside or inside vertebrate host or inside an invertebrate host.