Leishmania tropica
Location and host
- Found in skin of dog and man
- Vector: Sand flies (Phlebotomus sps.)
Morphology
- Indistinguishable form Leishmania spp. And Trypanosoma cruzi.
- A mastigote stage is round to oval , 1.5- 4µm in diameter
- Contains large nucleus and smaller kinetoplast

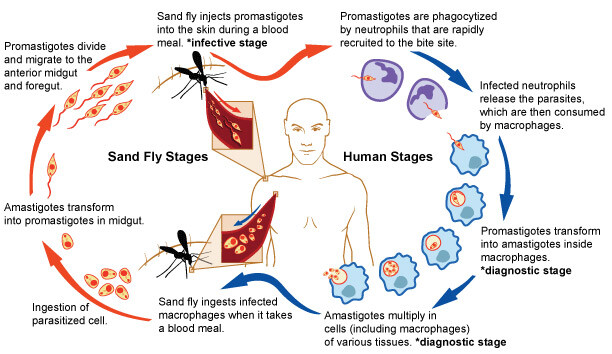
Life cycle
- After inoculation of parasite by vector, parasite grows and multiplies within macrophages and histocytes of skin at site of bite
- Promastigote changes into amastigote form
- These are taken up by flies and reaches to gut of sandflies
- Multiplies rapidly by binary fission and migrate back to proboscis
Pathogenesis
- This causes cutaneous leishmaniasis. Disease is also called ‘oriental sore’, ‘Delhi boli’, ‘ mucocutaneous leishmaniosis’ or ‘old world cutaneous leishmaniosis’.
- Cutaneous leishmaniosis is differentiated as dry or moist or mildly ecothymatous. Dry form is more common in dogs while moist form is prevalent in gebrils and other rodents.
- In dry cutaneous form, promastigote forms, introduced into the skin by sand fly are taken up by macrophages
- In macrophages, they multiply
- After maturity, resultant amastigote forms are released after rupture of cells and infect other cells.
- Lesions are detected after 3-6 weeks of bite of sand fly as a reddish papule, which gradually develops into a crust, forming shallow ulcer.
- Ulcer gradually enlarges. They may coalesce and spread over large areas. In uncomplicated case, ulcers may heal in 2-12 months, leaving deeply pigmented, depressed scar. Skin lesion are similar to that in man.
Diagnosis
- Organism are detected in epithelial and mononuclear cells by microscopic examination of material taken from the edge of an ulcer or a local lymph node. Biopsy material is taken if organisms are not detected in ulcer scrapings.
- Culture of materials in NµNCNOvyy-McNeal-Nicolle) medium
- Gel diffusion and passive agglutination test
Treatment and control
- Lithium antimony sulphate is given intramuscular, 1 ml raising by 0.5-2.5 ml in subsequent injection given on alternate days 4-6 times.
- Anti-biotics may be given to check secondary infection
- Control of population of sand flies.
Muco-cutaneous Leishmaniasis or Euspondia
- It is due to brasiliensis
- Not seen in Nepal and India, but causes severe and horrible skin lesions in mucous membrane of mouth, nose and pharynx
- Take long time to heal up