Isospora felis
Location and host: Found in small intestine of cat
Morphology
- Oocyst are ovoid, measuring 43×32 µm with smooth, yellowinsh to pale brown wall without micropyle, polar granules or residuum.
- Each sporulated oocyst contain two sporocyst. Each sporocyst consist of four sporozoites.
- Sporocyst are ellipsoidal; 20-27 x 17-22 µm with smooth colorless wall and prominent residuum.
- Sporozoites are sausage-shaped with clear sub central globules.
Isospora felis[i] - ESCCAP France](https://www.esccap.fr/images/coproscopie/sliders/_thumb1/oocyste-isospora-felis-2-cellules.jpg)
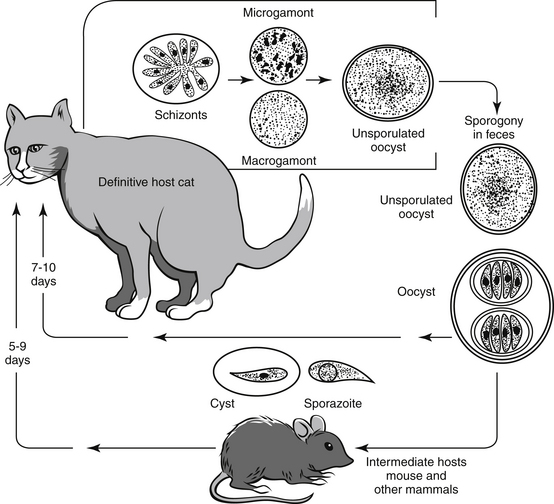
Lifecycle
- After ingestion of sporulated oocyst, cats get infected.
- After ingestion, sporozoites exits from oocyst in small intestine.
- Sporozoites undergo three generation of schizogony.
- Developmental cycle is through endodyogeny. Three types of meronts are produced. Mature first-generation meronts observed at 4 days PI and produce 16-17 merozoites.
- Mature second-generation meronts occur 5 days PI and produce about 10 merozoites.
- Third generation meronts were observed 6 days PI and occur in same host cell as in 2nd generation and produce 36-70 merozoites.
- Merozoites then starts sexual cycle. Macrogamonts and microgamonts produced, matured and produce macrogametes and microgametes. Gamonts appear from 6 days after infection.
- Microgamete fertilize macrogamete and results in formation of zygote; Zygote then develops wall around it and forms oocyst.
- Oocyst are discharged in faceces as unsporulated. Sporulation occurs outside host cells.
- Prepatent period: 7-10 days
- Patent period: 1-3 weeks.
Clinical signs/ Pathogenesis
- felis is moderately pathogenic for 6 week-12-week-old kitten
- Soft, mucoid faeces is observed in kitten 8 days after infection.
- Histopathogenic examination reveal erosion of superficial epithelial cells. After 7-9 days of infection, congestion, mild neutrophilic infiltration and hyper secretion of mucosa are observed.
- felis may cause severe disease in four-week-old kitten characterized by signs of enteritis, emaciation and death.
Diagnosis
- By finding different coccidial stages in intestine
- Demonstration of oocyst in faeces of cats
- Based on clinical signs
Treatment
- Treatment of coccidiosis in cats is practiced with sulfonamide and quinacrine.
- Sulphadimethoxine (SDM) @ 50 mg/ kg for 10 days or 55 mg/kg for 1 day and 27.5 mg/kg until signs disappear.
- Sulphadiazine and trimethoprim @ 25-30 mg/kg. Sukphadiazine + 5-10 mg/kg trimethoprim for 6 days for cats over 4 kg.
- Amproliumtiol : 300 – 400 mg/kg for 5 days
- Quinacrine : 10 mg/kg for 5 days.