Introduction
- Protozoa are unicellular organism belonging to animal kingdom in sense that they obtain their energy by intake of organic material rather than from radiant energy of sun by process of photosynthesis as seen in plant kingdom.
- All protozoa are eukaryotic type as they store their genetic information in chromosomes contained in nuclear envelope
Structure and function of protozoa
- All protozoa contain essentially a portion of protoplasm consisting cytoplasm and nucleus.
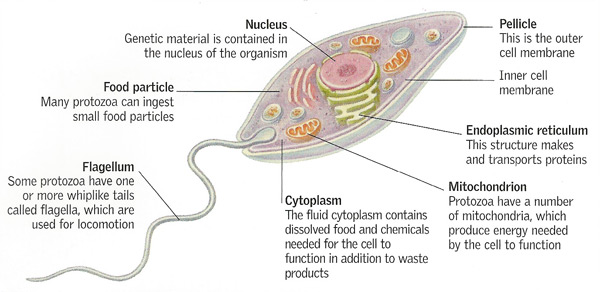
a. Nucleus
- Generally, nucleus in protozoa occur in two forms i.e. vesicular and compact.
b. Vesicular nucleus:
- This type of nucleus consists of nuclear membrane which bounds the nucleoplasm in which intracellular body lying more or less centrally called endosome or karyosome or nucleolus.
- Endosome lacks DNA whereas nucleolus contains DNA in it.
- In Case of Phylum Apicomplexa, this nucleus has one or more nucleoli that contain DNA.
- Chromatin material occurs on inner surface of nuclear membrane. It is seen as strands radiating from karyosome to the nuclear membrane.
- This nucleus is usually seen in sub-phyla mastigophora and Sarcodina.
c. Compact or massive nucleus
- This type of nucleus contains a large amount of chromatin and small amount of nucleoplasm.
- It may be spherical, oval, cylindrical, sausage-shaped, moniliform or horse-shoe shaped.
- It is found in amoeba proteus and in ciliates as macronucleus.
- Protozoa having two nuclei at any stage of their development, may either have twi similar nuclei or two dissimilar nuclei. Example:
I. Ciliophore having large nucleus (macronucleus) which governs cytoplasmic functions and smaller vesicular nucleus (micronucleus) which lies dormant in cell until sexual process of organism begin.
ii. Trypanosomes having trophonucleus which governs the general life of cell and another chromatic body called kinetoplast (kinetonucleus) which regulates locomotor function.
d. Cytoplasm
- It is extranuclear part of protozoa which is differentiated into:
I. Outer part called ectoplasm which are homogenous
ii. Inner part endoplasm that frequently contains granules, vacuoles and sometimes pigments.
- In sub-phyla, Sarcodina, there is no definite limiting membrane, whereas in other, pellicle serves this purpose.
- Cytoplasm may contain Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, ribosomes, lysosomes and other structures.