H. Canis
- Also reported from jackal, hyena, palm civet and cat.
Morphology
- Schizoints occur in the endothelial cells of spleen, liver and bone marrow. They are round or oval bodies, more or less filling the host cell and containing 30-40 nuclei.
- Gamonts are found in circulatory neutrophilis, ellipsoidal in shape about 11×4 µm, and are enveloped in a thick membrane.
- Schizoits include micromerozoites with defined nuclei, which in cross-section have ‘wheel-spoke’ appearance.

Fig: Wheel-spoke appearance of cs of schizonts including numerous micromerozoites
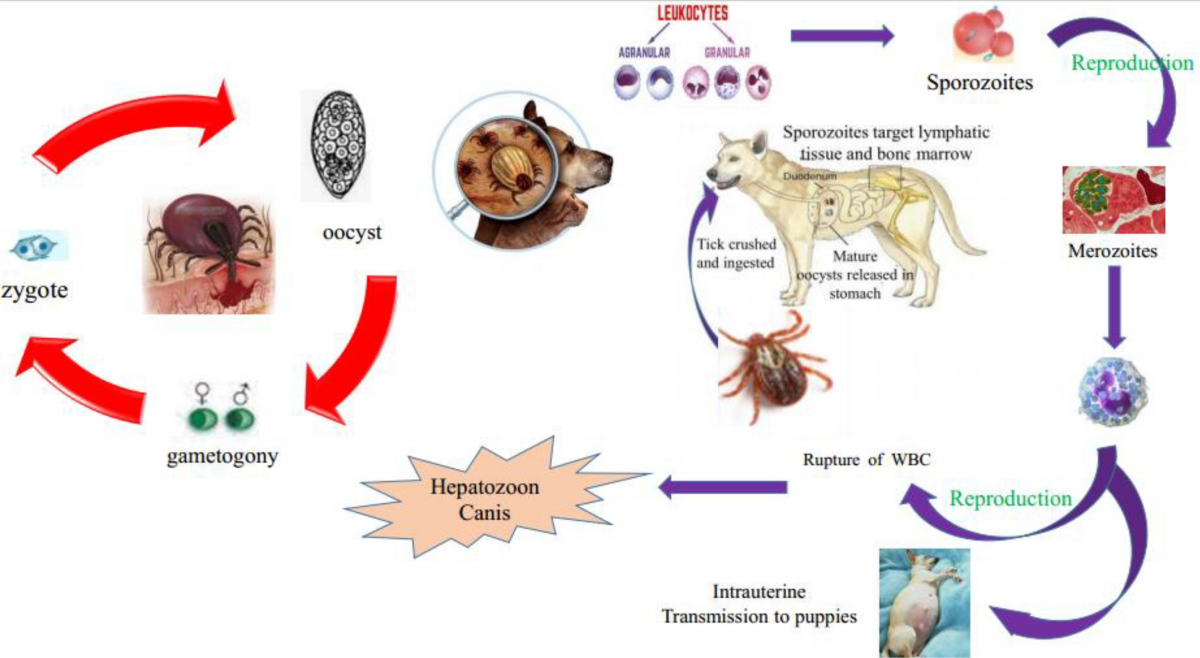
Life-cycle
- Life-cycle involve two hosts: Tick is final host in which syngamy occurs and dog is intermediate host in which asexual reproduction occurs.
- Dogs acquire infection when dogs ingest infected nymphs and adults of tick containing sporocyst in haemocoel.
- Sporozoites are liberated in intestine of dogs. Sporozoites penetrate intestinal wall and reaches spleen liver and bone marrow via blood stream.
- There they develop to schizonts. Two types of schizonts occurs.
- One produces few merozoites of large size (usually three and other produces large number of small merozoites, which later enter polymorphonuclear leukocytes.
- Merozoites forms gamonts in leukocytes which are elongate or rectangular bodies of size 8-12 µm x 3-6 µm surrounded by a delicate capsule. In citrated blood, these forms may be found free in plasma.
- Gaments in leukocytes are then ingested by R. sanguineus when feeds on infected dog.
- Gamonts are released in the gut of tick and undergoes sexual reproduction . Zygotes formed which are motile ookinetes.
- Penetrate intestinal wall of tick and enter haemocoel which grows to oocyst, with sporoblast and sporocyst.
- Each sporocyst produces 16 banana-shaped sporozoites . On ingestion of ticks, dog becomes infected.
Clinical signs
- Irregular fever
- Anaemia
- Loss of weigh
- Progressive emaciation
- Enlargement of spleen and lumbar paralysis also occurs
- Death occurs after 4-8 weeks of onset of clinical signs.
Diagnosis
- Based on clinical signs
- Based on PM findings: Enlargement of spleen, demonstration of parasite in myocardium of domestic cats.
- Demonstration of gamonts in blood smear.
- Demonstration of schizonts in spleen and bone marrow.
Treatment
- No treatment available
Prevention and control
- Control of ticks by regular grooming or use of ectoparasiticide.
Other species
a. H. americanum
- Gamonts present within neutrophils are ellipsoidal in shape, 8.8 x 3.9 µm with central compact nucleus and enveloped in a thick membrane.
- Cytoplasm stains pale blue and nucleus dark-reddish with Giemsa stain.
- Cyst in muscle are round to oval ; 250-500 µm in diameter, with outer portion composed of concentric layers of fine, pale staining laminar membranes, that give cyst ‘onion skin’ appearance.
b. H. muris
- Meronts in liver are 10-30 µm in diameter.
- Gamonts in lymphocytes appears as elongated oval bodies in stained blood smears.