Avian Malaria
Causative agent: Plasmodium gallinaceum
Location and host:
- Primarily parasite of domestic fowl in India and Nepal, but other birds can also be infected.
- Pre-erythrocytic phase is found in macrophases of skin, erythrocytic phase is found in RBCs and Exoerythrocytic phases found in endothelial cells and reticuloendothelial cells of spleen, brain and liver.
- Sexual reproduction in culex mosquitoes.
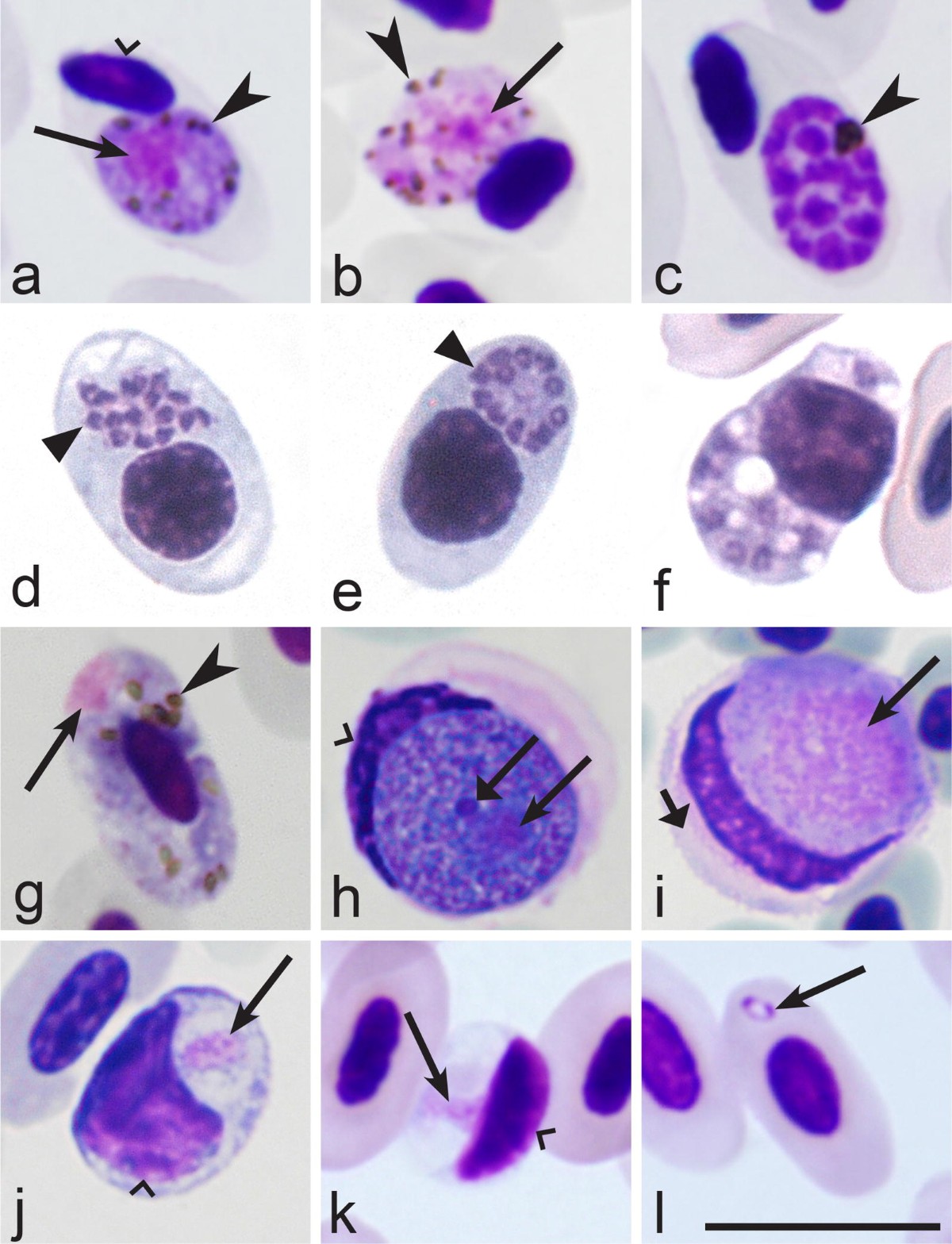
Morphology
- Trophozoite is small rounded form containing large vacuole, which displaces the cytoplasm of parasite to periphery of the erythrocyte.
- Nucleus situated at the one of the poles, giving young form “signet-ring” appearance.
- Both gametocytes and meronts can be round, oval or irregular in shape. Each meront produces 8-35 merozoites.
- Oocyst is about 50-60 nm in diameter and size of sporozoite is about 15 µm
 in length.
in length.
Lifecycle
- It completes in two host; Asexual reproduction occurs in vertebrate host and sexual reproduction takes place inside vector.
- Lifecycle in host starts when culicine mosquitoes introduce infective sporozoites into host through inoculation.
- After inoculation, pre-erythrocytic meronts cryptozoites are found in macrophages and fibroblast of skin near point of entry.
- From these cryptozoites, second generation pre-erythrocytic meronts (metacryptozoites) are formed. They mature at about 12 hours.
- Merozoites from metacryptozotes then enter erythrocytes and cells of lymphoid macrophage system in skin, spleen, lungs and capillary endothelial cells of major organs.
- Erythrocytic cycle is initiated at 7-10 days after infection by merozoites.
- Merozoites then rounds up to form trophozoite. These trophozoites undergoes merogony to produce merozoites.
- Merozoites released when infected erythrocyte rupture invades other erythrocytes and undergoes schizogony.
- Merozoites from metacryptozoites in macrophages, lymphoid system starts exo-erythrocytic schizogony, which further produce merozoites. These merozoites may start schizogony in RBC.
- Merozoites in RBC then initiate gamete formation simultaneously while invading other RBCs.
- During gametogony, microgametocytes and macrogametocytes are formed.
- These gametocytes then enter into mosquito, when mosquito comes to infected animal to take blood meal.
- After ingestion, nucleus of microgametocyte divides and through ex-flagellation, thin , 6-8µm long, flagella-like microgamete exits parent cell, swim away to find and fertilize macrogametocyte.
- After fusion, zygote is formed. Zygote then elongate to form ookinetes (Cone-shaped).
- Ookinetes then penetrates gut wall of mosquito, reaches haemocoel where oocyst are formed.
- Oocyst ruptures and liberates sporozoites into body cavity of mosquito and reaches to salivary gland of mosquito. They infect new host when mosquito takes a blood meal.

Note:
- Chills and fever repeated in case of malaria is due to continuous destruction of RBCs by merozoites during its multiplication.
- Mosquito remains infected for life and transmits the infection every time it sucks blood of birds.
Mode of transmission
- Through bite of infected mosquitoes.
Pathogenesis
- Chicks are more susceptible than adult birds.
- Affected birds shows progressive emaciation and anemia.
- Spleen and liver become enlarged.
- Glomerulonephritis in acute cases.
- Paralysis due to massive number of exoerythrocytic forms in endothelial cell of brain capillaries. Cerebral stoke due to blockage of capillaries may cause death.
Diagnosis
- On basis of clinical signs: Anemia, Emaciation and Fever.
- PM findings: Splenomegaly, Hepatomegaly
- Blood smear examination: Demonstration of parasites in blood smears by Giems or wright-Giemsa stain.
Chemoprophylaxis
- Varies with stages of developing inside host
- For schizonticides: Chloroquine @fmg/kg bwt and paludrine @ 7.5 mg/kg bwt for 3 successive days.
- Pyrimethamine @0.3 mg/kg for protecting chickens.
Preventions and control
- Control of mosquitoes at poultry farm through use of suitable insecticidal sprays
- Prevention of mosquitoes breeding by Buring stagnant water places
Other protozoan of avian species
- Plasmodium relictum : pigeon, dove, duck
- Plasmodium hermani: Turkey, Wild birds
- Plasmodium durae : Turkey, pea fowl
- Plasmodium juxtanucleare: Chicken
 in length.
in length.