Spirochaetosis :
- Avian intestinal spirochaetosis ( AIS ) is an acute , febrile, septicaemia, bacterial disease that affects a wide range of birds.
- It is characterised by chronic diarrhoea in diseased birds, and subsequently results in faecal staining of egg and wet litter.
- It results from colonization of caeca and rectum by one or more species of anaerobic spirochaetal bacteria .
- Also called Tick fever or Tick paralysis.
Etiology :
Borrelia anserina
Transmission :
- It is transmitted by arthropods eg : Argas persicus ( tick) and occasionally by infected faeces.
- Diseases are more prevalent where poultry ticks are found .
- Directly between birds by faecal-oral route
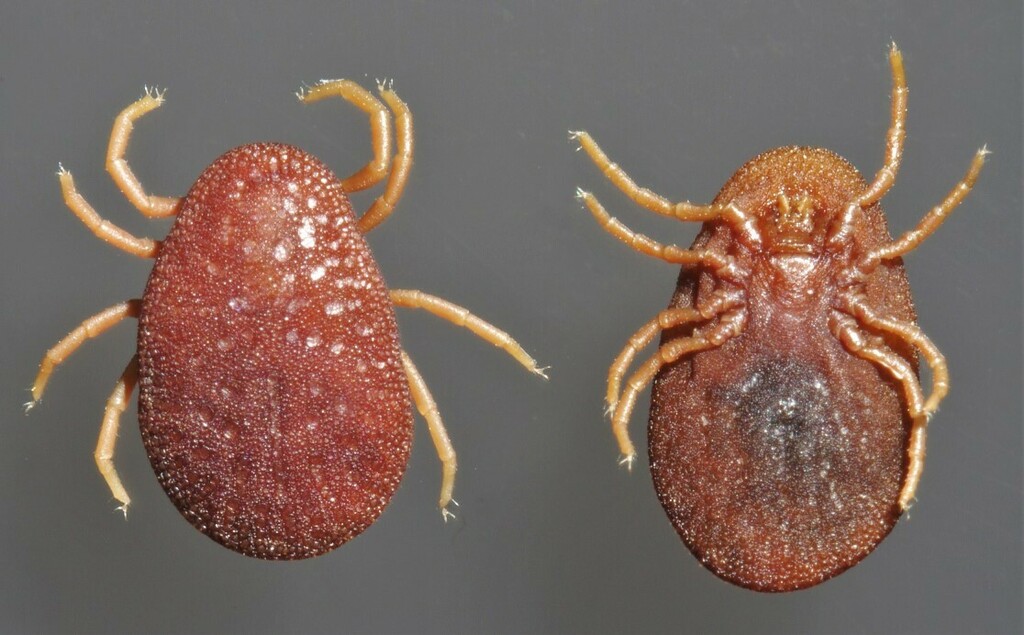

Fig : Argas persicus
Host range :
- Mainly affect poultry and turkey
- Also occur in geese,ducks,pheasants,sparrow and crow
Effect on bird varies :
- Weight of infection
- Other factors
- Diet ( quality of wheat /other feed )
- Management of related factors ( onset of egg laying ,moulting , floor housing , overcrowding , and other stresses)
- Genetics and concurrent infection with other disease agents.
Signs :
- Depression
- Anorexia
- Cyanosis of comb and wattle
- Thirst
- Often diarrhoea ( greenish) with excessive urates
- Weakness and progessive paralysis
- Drop in egg production in both systemic and intestinal forms
- High fever
- Jaundice
- Inco-ordination / paralysis of legs and wings.
Postmortem lesions :
- Marked splenomegaly with mottling
- Spleen mottled with ecchymotic hemorrhage
- Liver enlarged with small haemorrhage
- Necrotic foci
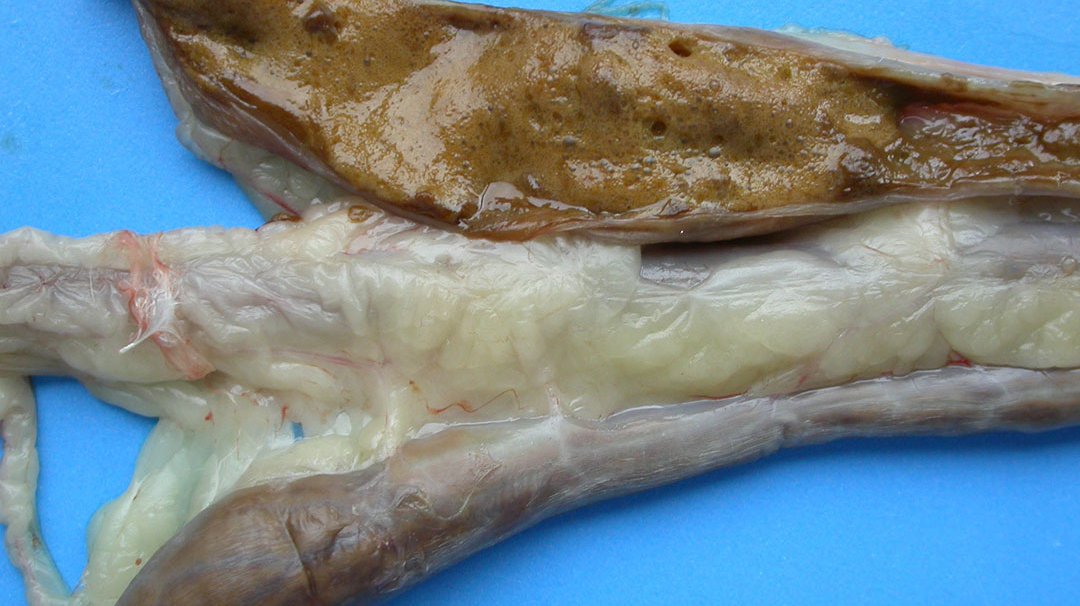
- Mucoid enteritis ( green- catarrhal enteritis)
- Hemorrhage in proventriculus
- Presence of tick in skin
- Kidney may be enlarged and pale

Microscopic lesions :
- Spirochaetes may be visible in caecal lumen or colonizing the epithelium
- Penetration between and below caecal epithelial cells oe caecal epithelial cell erosion/ necrosis has been described .
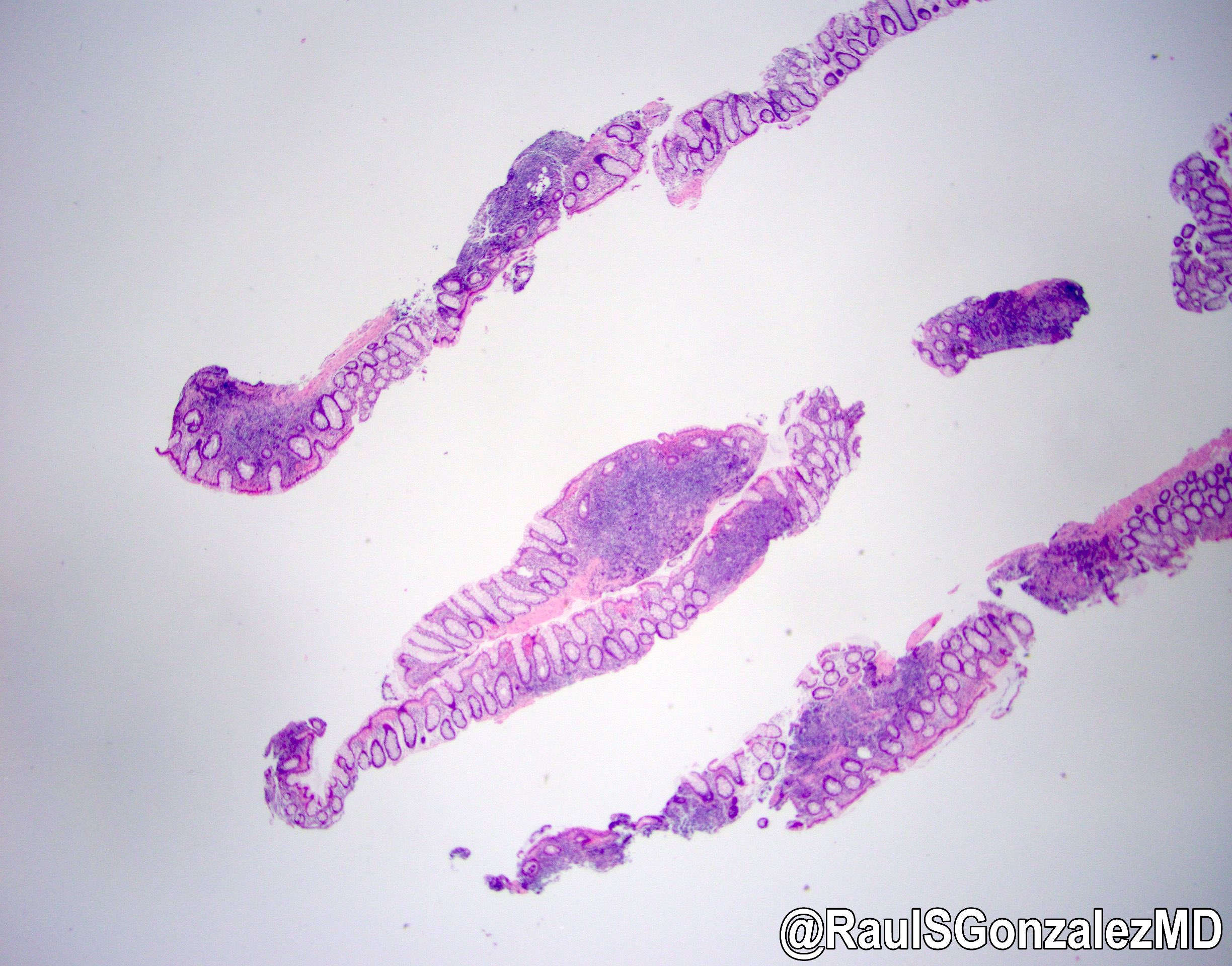
- Necrosis of hepatocytes
- Necrosis and depletion of lymphoid tissue in spleen and hemosiderosis
- Catarrhal enteritis
- Perivascu;lar gliosis in brain
- Hemorrhagic dermatitis
- Organism can be seen in liver section by silver stain
Diagnosis :
- History
- Clinical signs and symptoms
- Postmortem lesions
- Isolation and direct demonstration of intestinal spirochaetosis
- PCR testing
- Serological test [ Agar- gel diffusion ]
- Detection of spirochaetal antibody in yolks of eggs laid by infected hens
- Hematology
- Presence of tick infestation