Mycotoxicosis :
- The word mycotoxin stems from Greek word “mykes” which means mould and “toxicuum” means poison.
- Mycotoxicosis refers to all diseases caused by the effect of toxin produced by moulds.
- Disease is often subclinical and difficult to diagnose.
- Problems occur worldwide , but especially climates with high temperature and humidity and where grain is harvested with high water content .
Types of toxins :
a. Aflatoxins : produced by Aspergillus flavus
b. T2 fusarium toxin : by Fusarium spp.
[mouth lesion and thin egg shells ]
c. Ochratoxins : by Aspergillus ochraceus
[ interfere with function of kidney , proventriculus and gizzard ]
d. Rubratoxin : by Penicillium rubrum
[ interfere with thiamine metabolism and causes symptoms of deficiency ]
Species affected :
The species are with decreasing order of susceptibility :
Ducks , turkeys , geese, pheasants , chicken
Route of infection :
- Ingestion of fungal spores which are readily carried in air
(concentrate , silage or forage )
- Bedding
- Both fungal spores and formed toxins are highly resistant.
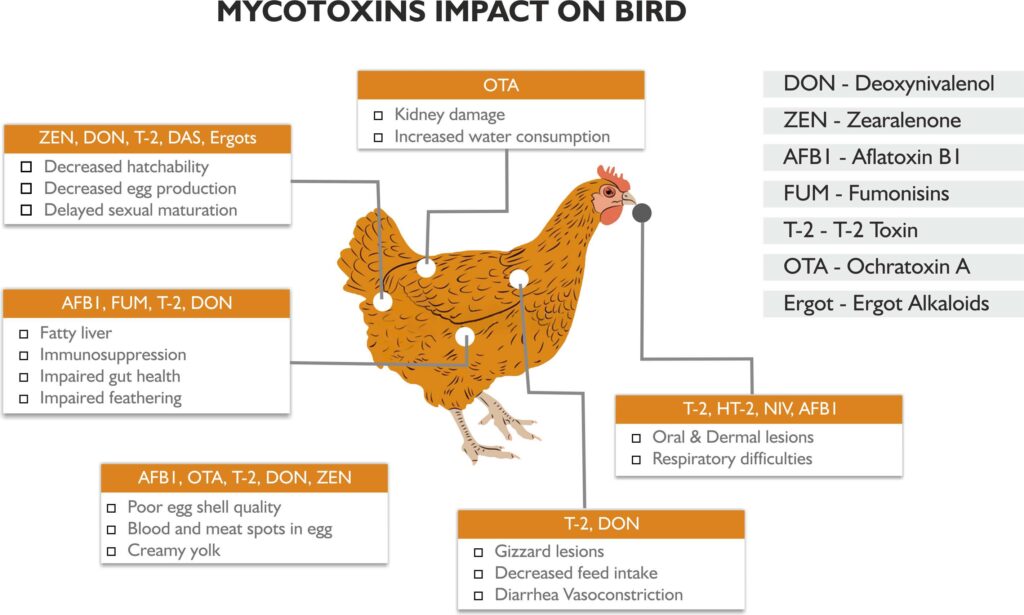
Mycotoxin exert their effects through four primary mechanism :
- Reduction of feed intake/ feed refusal .
- Alteration in nutrient content of feed in terms of nutrient absorption and metabolism
- Effect on endocrine and exocrine system
- Suppression of immune system
Fungi species :
a. Field fungi :
- Invade the seeds while the crop is still in the field .
- Include the species of :
- Fusarium
- Alternaria
- Cladosporium
- Diplodia
- Gibberella
- Helminthosporium
b. Storage fungi :
- They invade grains or seeds during storage.
- Species : Aspergillus , Penicillium
Signs :
- Signs vary with the species affected ; mycotoxin , the dose ingested and period of exposure
- Diarrhoea
- Paralysis / inco-ordination
- Reduced feed efficiency
- Reduced weight gain / egg production / hatchability
- Increased condemnation
- Pale shanks, combs, bone marrow

Fig : Oral lesions in poultry, including the tip of the tongue and the palate
and the floor of the oral cavity can be an indicator of a mycotoxin problem.
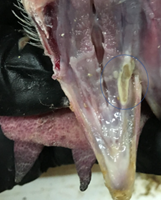
Fig : Oral lesions in poultry, such as the one circled here,
can be an indicator of mycotoxicosis.
Postmortem lesions :
- Lesions also vary in accordance with same factors as signs
- Mycotoxin can cause damage to mucosa with which they come in contact .
- They can also be absorbed and affect blood coagulation , resulting in petechiae and larger haemorrhages in various tissues.
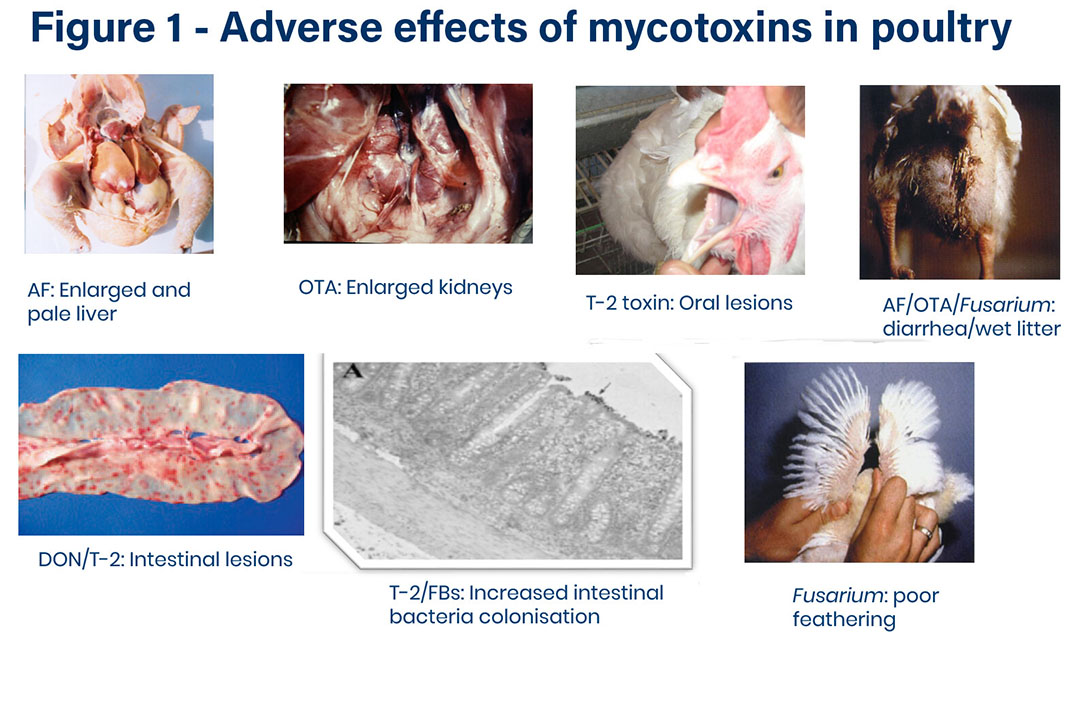
- Liver and kidney lesions :
Liver may be enlarged and fatty or show bile retention or tumor
- Enteritis of variable degree may be seen
- Hydropericardium
- Pale bone marrow
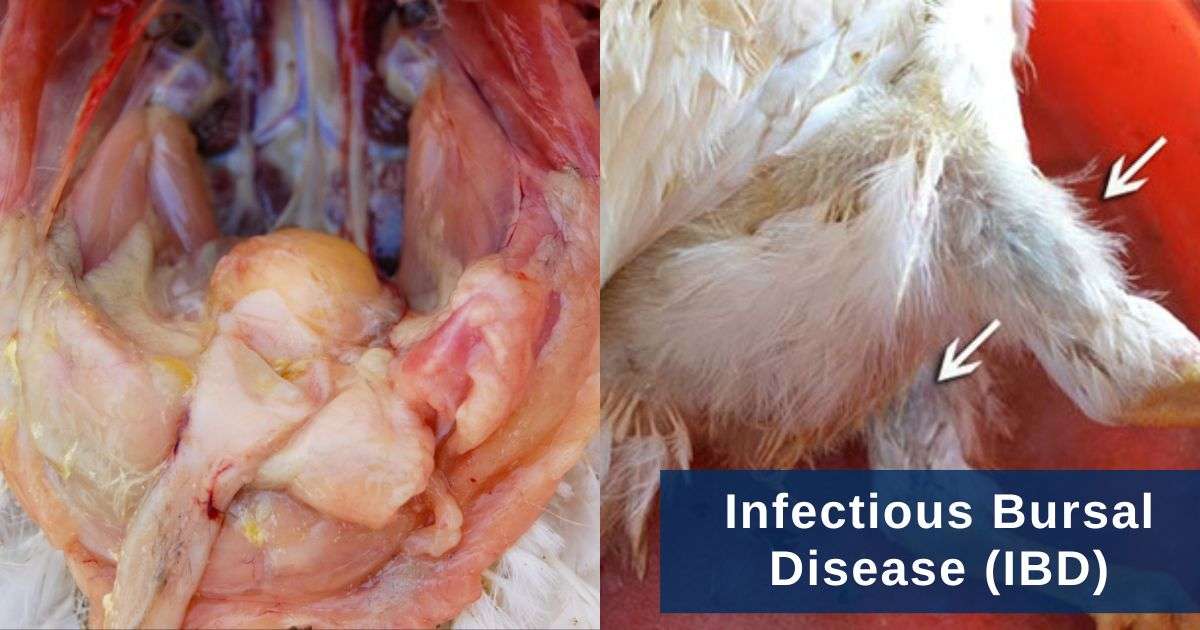
- Regression of bursa of fabricius
- Gizzard erosion


- Multiplication of moulds in cereals requires selenium and
This element is important for production of hepatic
lipases .
⬇
Aflatoxin inhibit synthesis and transport of lipid in liver
⬇
Fig : Fatty deposition in liver of a broiler Deficiencies of fat soluble vitamins ( A,D,E,K )
chicken with aflatoxicosis.
- Aflatoxin has been shown to be carcinogenic in rodents.
Diagnosis :
- History
- Signs and lesions
- Histology
- Identification and quantification of toxins in samples of feed or feed residue .
Differential diagnosis :
- Poor nutrition
- Poor management
- Physical damage to tissues
- Infectious bursal disease