Marek’s disease :
It is a lymphoproliferative disease of chickens characterised by mononuclear infiltration of PNS , other tissues and visceral organs.
- Due to neuronal involvement , synonyms used are : Polyneuritis , Fowl paralysis , Range paralysis and Neurolymphomatosis .
- Mainly found in chickens , but occasionally affect pheasants , quail , game fowl and turkeys .

Etiology :
Herpes virus [ enveloped , Ds DNA virus ]
- Classified into 3 serotypes :
- Serotype 1 : includes oncogenic strains of MDV
- Serotype 2 : includes naturally non – pathogenic strains
- Serotype 3 : antigenically related to herpes virus of turkey (HVT) . Used for production of vaccine k/a HVT126
- Serotype 1 again subclassified into :
- Mildly virulent (mMDV)
- Virulent (vMDV)
- Very virulent (vvMDV)
- Virus infectivity is strictly cell associated except in feather follicles epithelium where cell free viruses are produced .
Transmission :
- Virus is present in desquamated feather follicle epithelial cells , oral , nasal , tracheal secretion .
- Feather follicle : main source of infectivity of dander
- Air borne route is the most important route
- Virus is not transmitted through eggs .
- Infected birds continue to contaminate the environment by shedding viruses .
- Females are more susceptible than men .
- Stress is the main environmental factor .
Pathogenesis :
Four phases of infection are recognized :
- Early cytolytic infection ( productive – restrictive )
- Latent infection : immune development and T-cell ( mainly) affected ; B-cell are also affected .
- Second phase of cytolytic ( productive – restrictive infection coincident with permanent immunosuppression )
- Proliferative phase ( involving non-productively infected lymphoid cells that may or maynot progress to point of lymphoma formation )
Inhalation of Virus particles
⬇
Growth of virus particles within cells of lungs
⬇
Within 3-4 days ; cytolytic phase occur in lymphoid organs
[ destruction of lymphocytes mainly in Bursa of fabricius , thymus & spleen ]
Primary target cell in all these organ – B-lymphocytes
⬇
After 6-7 days ; latency ( latent phase )
Interference with immune response and infect T-lymphocytes
⬇
Virus spread throughout body by infected lymphocytes and is present in blood in cell associated form [ viremia]
⬇
After 2 weeks of primary infection ; second phase of cytolytic occurs 9in feather follicle and remains in free form ( set free virus ) capable of producing infection and shed in the environment in feather debris and danders .
Here dander like material is produced which acts as source of infection
⬇
Proliferation of lymphocytes – final response and progress to tumor formation .
⬇
T- lymphocytes transform into tumor cells and proliferate in nerve , other tissue and organs.
⬇
This results in infiltration of these cells in nerves and lymphoma .
⬇
Death of birds from lymphoma at any time 3 weeks onward .
Various forms of disease :
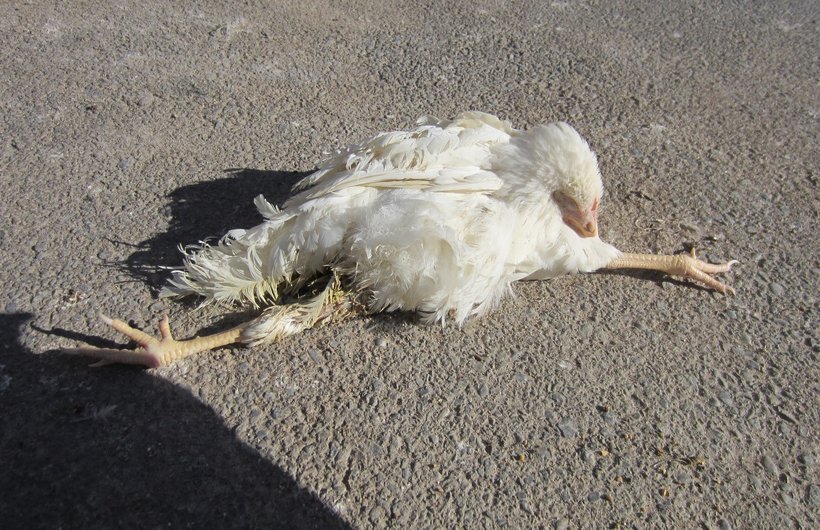
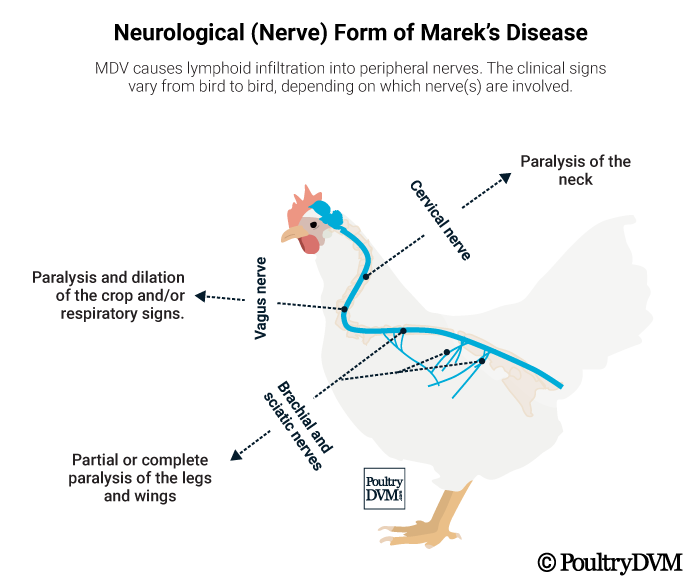
a. Neurological :
- Paralysis
- Dropping wings
- Extended legs
- Torticollis
b. Ocular :
- Blindness
- Distorted iris shape
- Discoloured iris ( iris may become whitish – Grey eye syndrome

c. Cutaneous :
- Enlarged feather follicles ,
- Leg lesion
d. Visceral :
- Nodular diffuse visceral lymphoid tumors

Clinical signs :
- Affects birds from about 6 weeks of age , mainly 12-14 weeks
- IP = 3-4 weeks
a. Acute MD :
- Mortality : 10-30%
- Birds may die suddenly or,
Showing signs of dullness , depression or respiratory distress if heart is involved.
b. Classical MD :
- Mortality : 10-15 %
- Signs depends on peripheral nerves affected :
c. Brachial and sciatic nerves :
- Progressoive spastic paralysis ( i.e. paralysis accompanied by muscular rigidity ) of wings and legs.
- Purplish discolouration of leg skin ( Red leg syndrome )
- Inco-ordination is a common early sign : one leg is held forward and the other backward because of unilateral paresis or paralysis .
d. Cervical nerves : torticollis ( twisting of neck )
e. Vagus and intercostal nerve : respiratory signs
fig: Asymmetrical paralysis
fig: torticollis in marek disease
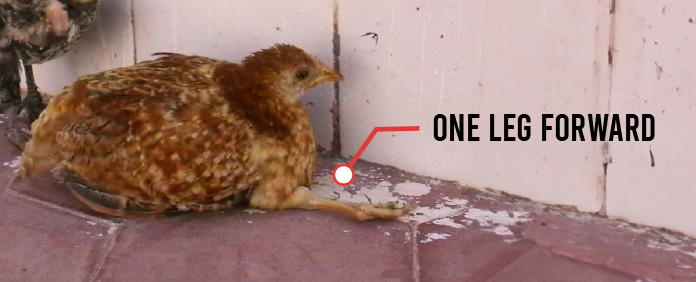

fig: Ulcer in feather and follicle
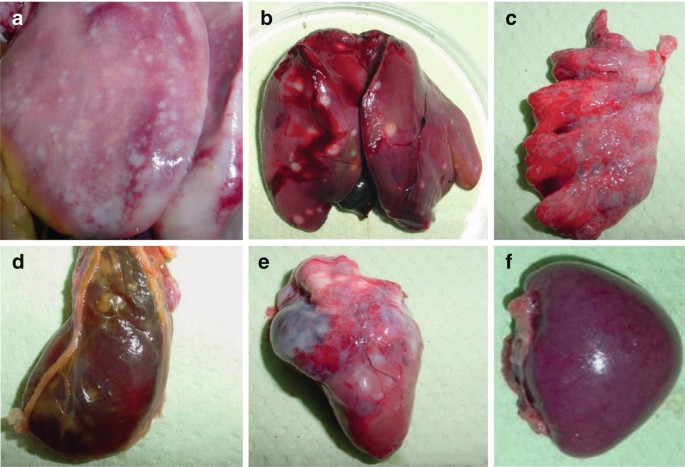
Gross lesions :
- Enlargement of one or more peripheral nerves, affected nerves are upto 2-3 times the normal thickness .
- Nerves commonly affected are brachial and sciatic plexus , coeliac plexus , abdominal vagus and intercostal nerves .
- Lymphoma / tumor ( cauliflower like growth ) usually in ovary but also in lungs , kidney , heart , liver , skin , feather follicles ( skin leukosis and muscles)
- Diffuse lymphomatous involvement and enlargement of liver , gonads , spleen , kidney , lungs , proventriculus and heart .
- Bursa : usually atrophic or some do develop diffuse thickening .

Microscopic lesions :
- There types of lesions in peripheral nerves :
- Cellular infiltration of nerves with mature lymphocytes
- Separation of nerve fibre associated with edema
- Nerves are infiltrated with lymphoblasts
- CNS : myelin degeneration of nerves , perivascular cuffing , schwann cell proliferation
- Necrosis of follicles of bursa of fabricius is commonly seen and cyst are also seen
- Diffuse infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells in affected organs
- Mainly , T-lymphocytes are present .

Diagnosis :
- History
- Clinical signs and lesions
- Age affected
- PCR
- Serological test : AGPT , Viral neutralization test , FAT
- Radial immunodiffusion test
- Histochemical staining
- MATSA ( MD associated Transforming Surface Antigen )
Non specific MD virus antigen ; also present in HVT vaccinated chicken . It is diagnostic antigen.
DDx :
- Lymphoid leukosis
- Botulism
- Deficiency of Thiamine
- Deficiency of Ca / P / Vit D , especially at start of lay
