Gumboro disease
[ Infectious bursal disease , Infectious bursitis , Infectious avian nephrosis ]
- An acute contagious viral disease of young chickens , caused by infectious bursal disease viral (IBDV)
- Characterised by diarrhoea , vent picking , trembling , incoordination , inflammation followed by atrophy of bursa of fabricius
- Affects young chick usually 3-6 weeks of age
- Causes heavy mortality in chickens at 3-6 weeks of age
- Causes immunosuppression which leads to vaccination failure , E. coli infection , gangrenous dermatitis and inclusion body hepatitis

Etiology :
- IBDV is a Ds RNA virus
- Member of Birnaviridae family is a single shelled non-enveloped virion
Serotype :
a. Serotype 1 : Pathogenic
- Classical virulent strain
- US antigenic variant strains
- Very virulent strains
b. Serotype 2 : Non- pathogenic
- Meny vaccine strains derived from classical virulent strains
Source of infection :
- Infected houses remain infected for 122 days
- Water , feed and dropping from infected pen
- Litter , mites and meals worms
- Mechanical vector ( wild birds and humans ) also transmit the disease
- Litter used as manure spread disease in particular areas
Route of infection :
- Oro – pharynx
- Oral route
- Conjunctiva
- Respiratory tract
- No vertical transmission
- Infected birds shed virus for 14 days in their faeces . Feed , water and poultry house , litter become contaminated
Pathogenesis :
IBDV ➦ enter through oro-nasal route
⬇
Replication in the macrophages and lymphatic cells of respiratory tract , duodenum , jejunum, caecum , etc
⬇
Bloodstream ( viremia)
⬇
Target organ
⬇
Bursa of Fabricius
⬇
Active replication in the bursal follicles and B-cells
⬇
Bloodstream (secondary viremia)
⬇
Leads to infection in muscles , kidney ,etc causing clinical signs and death
- Immature B-lymphocytes in the follicles of bursa are target cells of viral replication
- By 13 hours PI, most follicles in the bursa are virus positive
- By 16 hours PI, a second massive viremia occurs
- There is infection and secondary viral replication in other lymphatic organs
- Clinical disease and death occurs within 64-72 hours PI
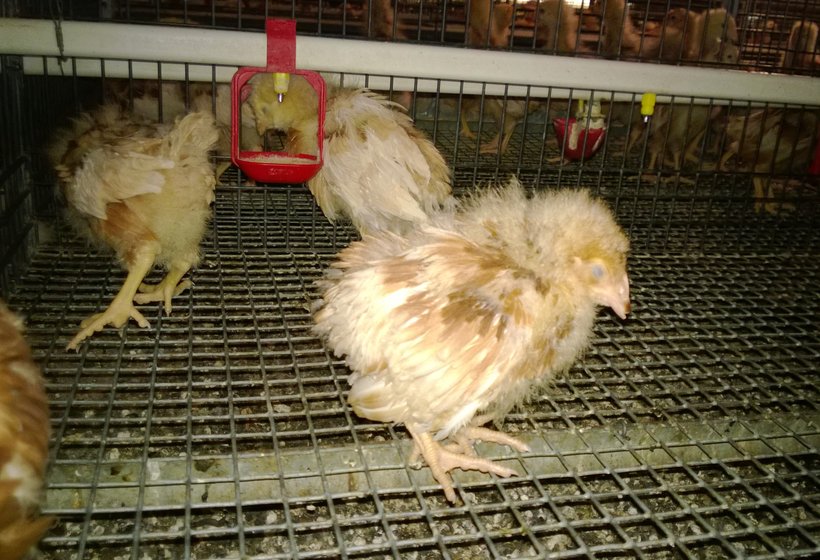
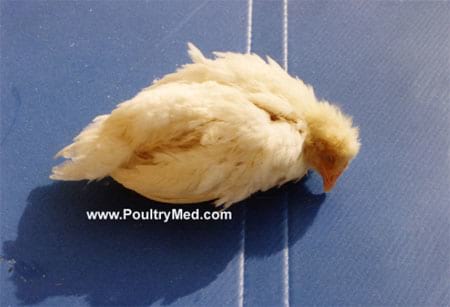
Clinical finding :
a. Clinical form :
- Occurs between 3-8 weeks of age depending on maternal antibody production
- Depressed
- Pale , huddling near heat source
- White watery diarrhoea
- Soiled vent feathers
- Vent picking
- Inflammation of cloaca
- Disease may appear suddenly and morbidity typically reaches 100%
- Mortality varies ranging from 5-10% but can be as high as 60% depending on pathogenicity of strain involved
- Highly pathogenic strains – “ very virulent” IBD (vv IBD) resulting in high mortality


b. Subclinical form :
- Before 3 weeks of age.
- Early IBD infection result in permanent immunosuppression without mortality
- Immunosuppression is economically important due to increased susceptibility to secondary infections especially in respiratory tract
- In broilers , disease results in bad performance with lower weight gains and higher feed conversion ratios .
Postmortem lesions :
- Bursa of fabricius – enlarged and haemorrhagic
- Hemorrhages in skeletal muscles especially in thigh
- Dehydration
- Swollen kidney with urates
- Haemorrhages in the junction between proventriculus and gizzard


Microscopic :
- Destruction of lymphocytes in bursa of fabricius of infected animals

Fig: The affected bursal section showing infectious bursal disease viral antigens in the lesion sites identified in bursal follicles (Immunohistochemistry, ×4).

Fig: Cystic changes evident in the medullary region in the bursal follicles (H and E, ×10).
Diagnosis :
- History
- Clinical signs and lesions
- Histopathology
- Virus isolation and identification
- FA techniques
- PCR : for detection of viral genome
- Serological test : Agar gel precipitation and ELISA for detecting antibody
Differential diagnosis :
- Coccidiosis
- ND
- Vit A deficiency
- Fatty liver
- Kidney syndrome
- Hemorrhages syndrome in muscles