Fowl pox :
[ sore head , Avian diphtheria , bird pox ]
- It is contagious slow spreading viral disease
- Birds of all age is affected, mainly chickens and turkey
- Some viral type may also affect pigeon , geese , pheasant and quails
- Mortality rate = 1-2%
- IP = 2-3 weeks
- Fowlpox is seen worldwide
- There are 2 forms :
- Wet form is characterised by plaques in mouth and URT
- Dry form is characterised by wart-like skin lesions that progress toi thick scabs

Etiology :
- The largest Ds DNA virus , an Avipoxvirus belongs to Family Poxviridae
- Enveloped and brick shaped virus
- Virus is highly resistant in dried scab and under certain condition may survive for months
Transmission :
- Mosquitoes are the most common vectors for transmission of avipoxvirus
- Virus can also be transmitted indirectly by contaminated surfaces or airborne particles
- Contaminated water and feed
- Scales of disease bird also transmit the disease
- Through wound
- Vertical transmission is suspected
- Recovered birds do not remain carriers
Clinical signs :
a. Cutaneous form (dry form):
- Wart like growths are seen on face , comb , wattle and featherless part of body
- They grow readily and then yellow and later turn black / brown lesion
- After 2-3 weeks ; lesions dry up and scabby
- In some cases , lesions are limited chiefly on feet and legs
- Cutaneous lesions on eyelids may cause complete closure of one or both eye

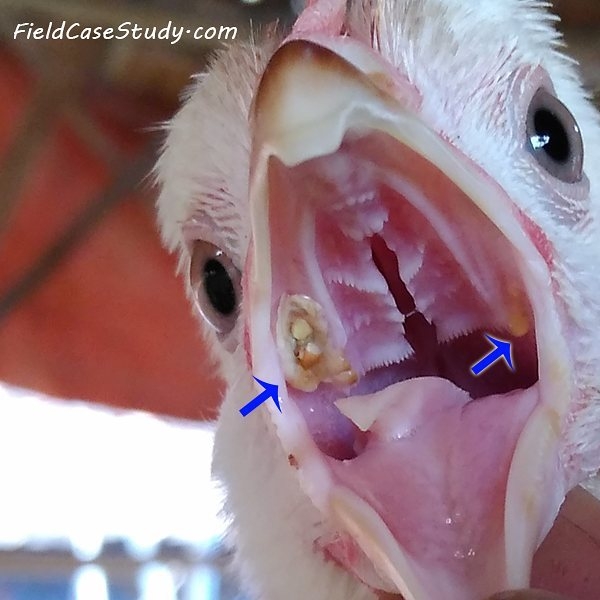
b. Diphtheritic form 🙁 wet form )
- White patches or slightly elevated nodules occur inside the mouth and tongue . This merges together to form raised – yellow cheesy patches
- Mucous membrane of mouth and esophagus are affected
- Breathing may be difficult
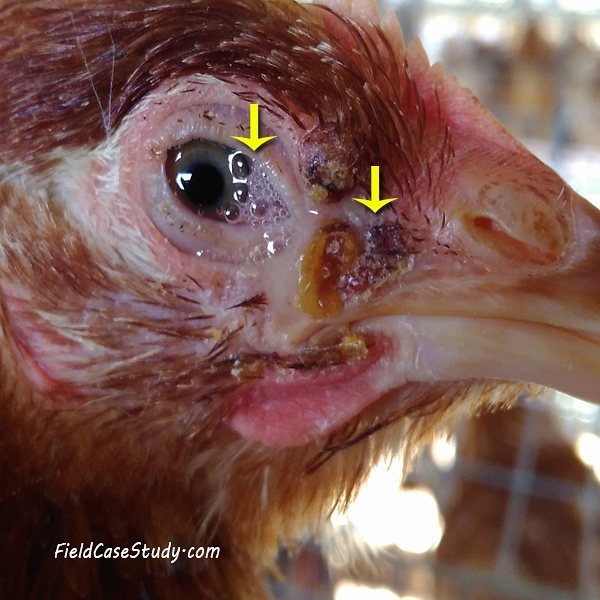
c. Oculonasal form :
- Eruption on the opening of eye and nose
- Ear and nose may smell and discharge from eye and nose may be seen
- Affected bird won’t eat and difficulty in swallowing
Postmortem lesions :
- Diphtheritic form is recognised by presence of nodular hyperplasia of mucosa of pharynx and trachea
- Chicken which die of diphtheritic pox may show a plug of desquamated epithelium which lodge in glottis resulting in asphyxiation
Diagnosis :
- History
- Clinical signs [ cutaneous lesions are characteristics ]
- Physical exam
- Histological examination of affected tissue will confirm the presence of intracytoplasmic inclusions ( Bollinger bodies ) in respiratory mucosa and skin
- PCR
- Pox virus – virus isolation , FA test , electron microscopy , agar gel immunodiffusion of scab with underlying epithelium , URT or nodilar lesions
DDx :
- Necrotic dermatitis
- Leg mites
- Thrush and canker