Fowl cholera :
It is a contagious, bacterial disease that affects domestic and wild birds worldwide ( turkey and waterfowl are more susceptible than chicken ).
- It usually occurs as a septicaemia of sudden onset with high mortality and morbidity , but chronic and asymptomatic infection also occur .
- Older chicks are more susceptible .

Etiology :
Pasteurella multocida type A
( small, gram negative , non-motile with a capsule that exhibit pleomorphism after repeated subculture ; give bipolar appearance when stained with Wright’s stain )
Transmission :
a. Direct contact with infected birds
- Secretions made from infected birds ( mouth, nose , conjunctiva, ete )
- Close contact with one another
b. Ingestion
- Through contamination of the environment , feed or water with faces from the infected host.
c. Predator attacks
- Non fatal predator attack from wild or domestic animals ( dog/cat – carrier of bacteria in oral cavity )
d. Fomites : contamination of equipment , clothing , cages, feeders
e. Aerosol form
- multocida can persist in env. For weeks after the outbreak.
Pathogenesis :
Entrance through URT mucosal membrane , conjunctiva , cutaneous wound
- Start of acute septicaemia with coagulopathies.
- Production of endotoxin ; endothelial damage ; edema , haemorrhages , shock, sudden death
- Bacteremia ; spreading to lung
Clinical signs:
a. Acute form :
- Sudden changes in mortality without previous signs
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Ruffled feathers
- Mucous discharge from mouth
- Green watery diarrhoea
- difficulty
- blue/purple colouration of skin and swelling of comb / wattle
- Pneumonia is particularly common in turkey

Fig: green feces in fowl cholera
b. Chronic form :
- Signs are related to localized infection of wattles, joints, tendon sheath , foot pads; which often are swollen because of accumulated fibrinosuppurative exudate .
- Exudative conjunctivitis and pharyngitis
- Torticollis
- Failure of growth and development
- Drop in egg production
- Dermal necrosis in turkey

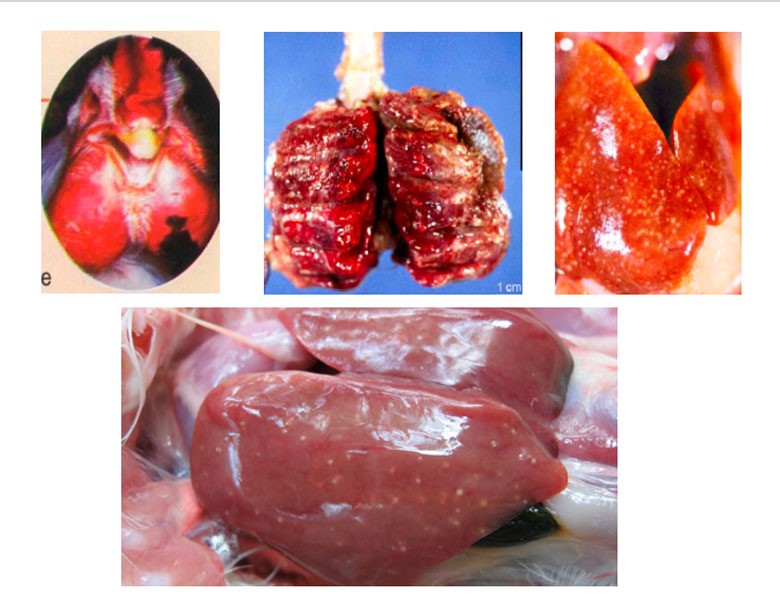
fig: lesions in fowl cholera
Postmortem finding :
- Peracute and acute forms :
- Disease shows primarily vascular disturbances
- General passive hyperemia and congestion throughout the carcass
- Petechial and ecchymotic haemorrhages in subepicardial and subserosal locations.
- Enlargement of liver and spleen
- Increased amount of peritoneal and pericardial fluids.
- Subacute form :
Multiple , small , necrotic foci may be disseminated throughout liver and spleen.
- Chronic forms :
- Suppurative lesions may be widely distributed, often involving resp. Tract , conjunctiva and adjacent tissue of head .
- Caseous arthritis and productive inflammation of peritoneal cavity and oviduct
- Fibronectin dermatitis
- Sequestered necrotic lung lesion
- Osteomyelitis
Diagnosis :
- History
- Clinical signs and lesions
- Isolation and identification of bacteria
- PCR testing
- Serological test : AGID , ELISA , whole blood agglutination , agar diffusion test
- Immunofluorescence microscopy
DDx :
- Erysipelas
- Septicaemic viral
- Infectious coryza
- Fowl typhoid
- Fowl plague ( avian flu )
- Duck plague