Avian mycoplasmosis :
Mycoplasma causes respiratory infection ( chronic respiratory disease) in chicken, turkey and other avian sps.
- Morbidity is typically high and mortality is low in affected flocks in uncomplicated cases; signs are generally more severe in turkey.
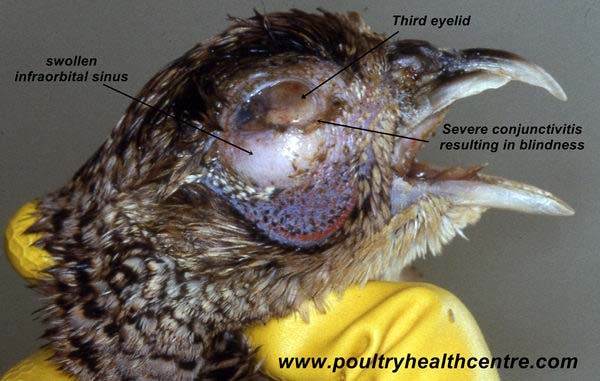
- In Turkey, it frequently results in swollen infraorbital sinuses; thus called “infectious sinusitis”.
Etiology :
- gallisepticum ( most pathogenic avian mycoplasma )
[ it is very small , lack cell wall so sensitized to antibiotic like
penicillin ]
- synoviae 🠞 causes infectious synovitis
In experimental cases ; IP = 6-21 days
Naturally IP = variable ; infected birds maybe asymptomatic until they
stressed
Transmission :
a. Horizontal transmission :
- Close contact between birds
- Aerosol spreads over short distances and can be responsible for transmission within a flock.
- Contamination of feed, water and environment .
- Fomites ( shoes, equipment)
b. Vertical transmission :
- Egg transmission occurs more frequent in birds infected during laying than n birds infected before they mature.
- Infected birds can be carriers and can remain asymptomatic until they are stressed .
- Stress condition :
- Infection ( bacterial , viral )
- Vaccination with live viruses
- Cold weather
- Crowding or poor air quality
- Concurrent infection ( newcastle disease , IBV , E. coli )
Pathogenesis :
When the organisms enter into body through route of inhalation
🠋
They bind to mucosal surface of upper respiratory tract ( trachea , bronchi , sinus )
🠋
Causes respiratory lesions
( tracheitis , bronchitis , sinusitis )
🠋
Activates host immune system and killed or neutralized by activation of B-cell and T-cell
( cell mediated immunity )
🠋
Some of them remains unkilled and remains in URT of chicken and turkey for long time
🠋
When there is stressed condition or concurrent infection with E. coli or NDV
🠋
Chronic respiratory lesions occurs
Clinical signs:
- Depression
- Slight to marked rales
- Coughing and sneezing
- Dyspnea
- Decrease weight gain , feed efficiency and egg production
- In turkey; swelling of infraorbital sinus
- In laying flocks; chronic increase in mortality and decrease in overall production rate

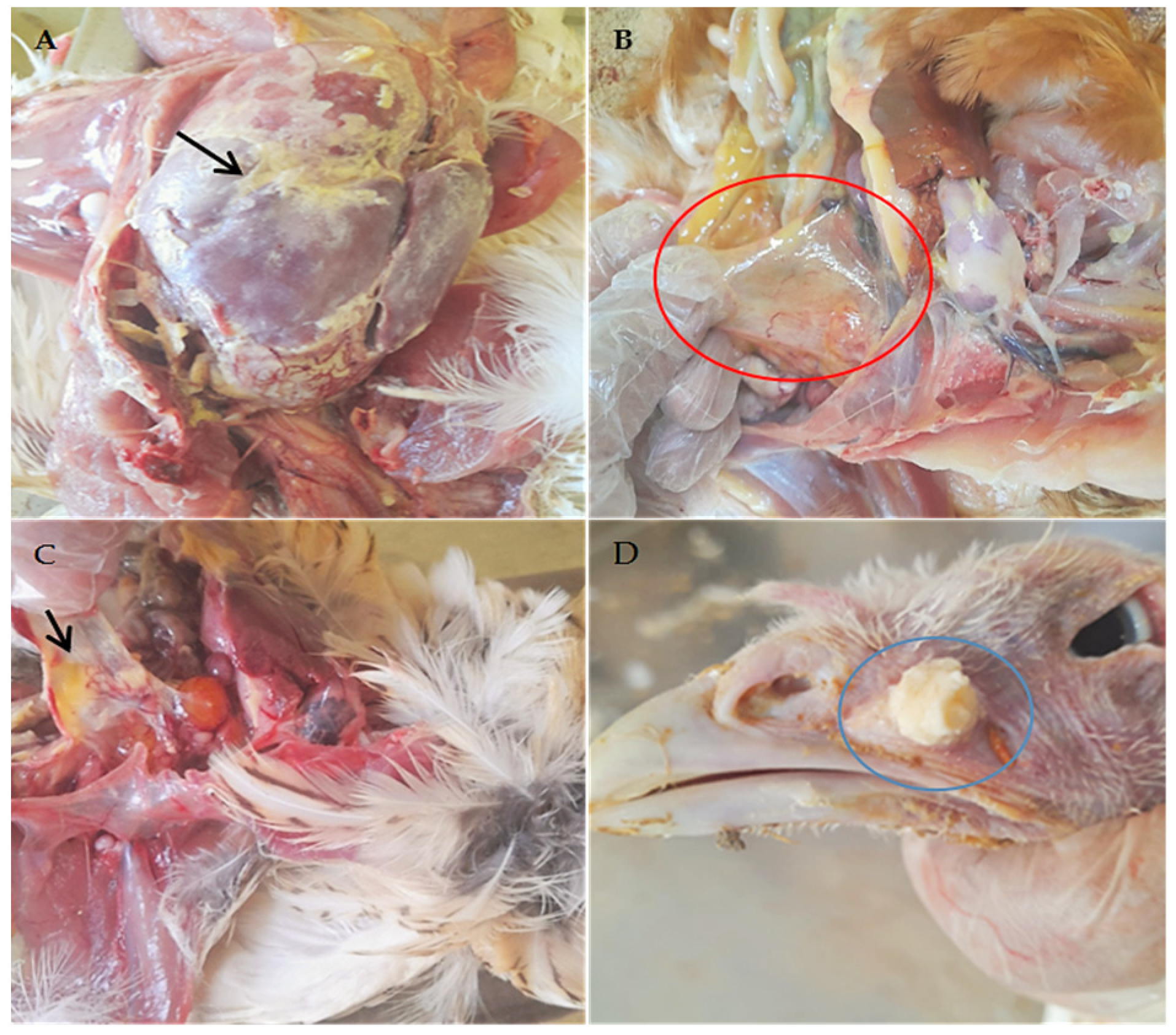
Postmortem lesions :
- In case of uncomplicated infection ; there is relatively mild catarrhal sinusitis, tracheitis and air sacculitis
- When E. coli infection occurs more concurrent ; there is severe air sac thickening and turbidity with exudative accumulation , adhesive pericarditis and fibrinous perihepatitis .
- Turkey ; severe mucopurulent sinusitis and varying degree of tracheitis and air sacculitis .



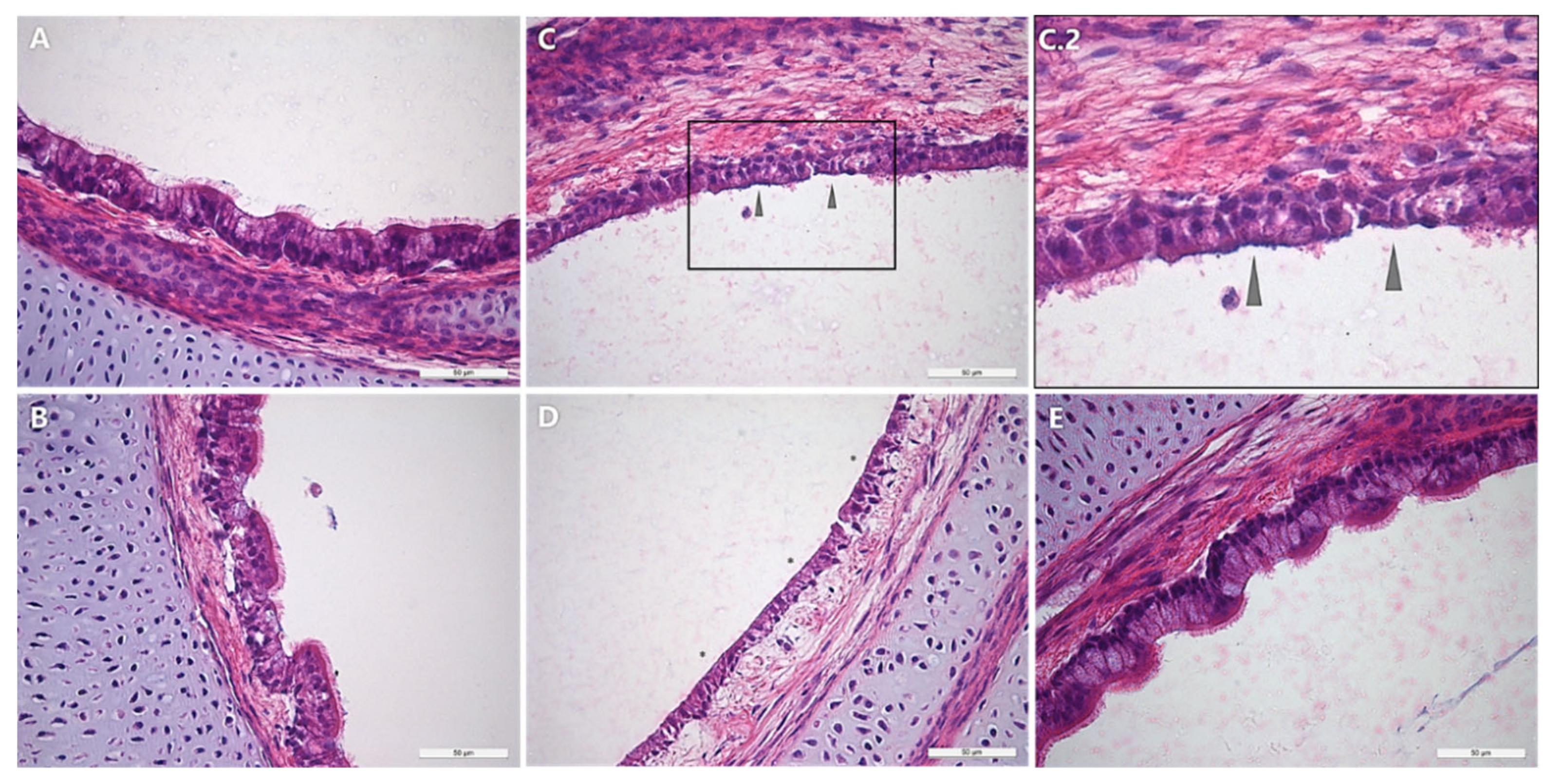
Microscopic lesions:
- Involved mucous membranes ( trachea , air sac ) are thickened, hyperplastic, necrotic , infiltrated with inflammatory cells, formation of lymphoid follicles.
- Mucosa lamina propria contain focal areas of lymphoid hyperplasia and germinal center formation
- Tubulo-alveolar elongation of tracheal glands
- Presence of lymphoid follicles in walls of air vesicles.
Diagnosis :
- History
- Clinical signs and lesions
- Isolation and identification of organism
- Serological test : HI test ( confirmatory test )
ELISA
- Molecular level test : Real Time- PCR ( RT-PCR )
[ due to its fastidious nature and difficulty in isolation ; it is method for
detection and characterization ]

Fig : Photomicrograph of air sac showing severe mononuclear cell infiltration along with few PMN and congestion
DDx :
- coli infection
- Newcastle disease
- Avian influenza
- Infectious bronchitis
- Fowl cholera