Avian lymphoid leukosis
Synonym : Avian leukosis , Big liver disease
- It is a neoplastic disease of chickens caused by a virus of leukosis / sarcoma group .
- Characterised by timor formation of bursa of fabricius with metastasis to other tissues and all abdominal organs .
- Lymphoid leukosis is a B-cell tumor which starts in bursa and before sexual maturity may spread to other organs .
- Mature birds are more affected , usually a problem of breeders and laying hens.
- There is marked enlargement of liver [ so called Big Liver Disease ]
Etiology :
- Caused by avian leukosis or sarcoma virus group of alpha – retrovirus
[ enveloped , ssDNA virus ]
- Most birds are exposed by sexual maturity .
Transmission :
- Both horizontal and vertical
- Cock may act only as a virus carrier and source of contact or venereal infection to other birds .
- Transmission can be reduced / eliminated by strict sanitation .

Pathogenesis :
Horizontal / vertical transmission
⬇
Malignancy in bursa dependent lymphoid system , early as 4-8 week after infection [ incubation]
⬇
Cells from Bursa of fabricius transform itself into cancerous type and then spread into different organs via blood/ vascular system
The transformed cells are called lymphoblasts
⬇
Lymphoblasts proliferate and give rise to nodular growth into bursa which are visible after 14 weeks.
Symptoms :
- IP = 4 months or more
- Inappetance
- Weakness
- Diarrhoea ( greenish in terminal stages)
- Dehydration
- Emaciation
- Infected chickens become depressed before death
- Comb may be pale shriveled and sometimes cyanotic
- Enlargement of abdomen , liver and bursa
- Many are asymptomatic
- Persistent low mortality

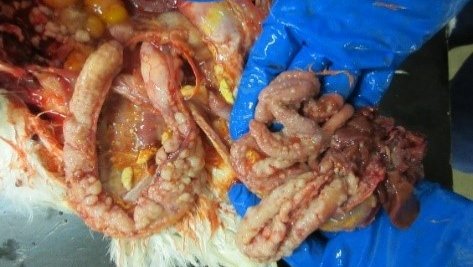
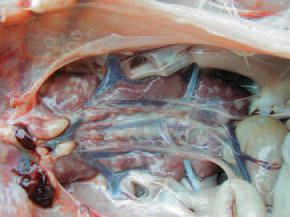
Postmortem lesions :
- Focal or diffuse white or gray neoplastic lesions are seen in bursa , liver , spleen and kidneys.
- External tumors may be seen and abdomen is enlarged and feathers are sometimes spread with urates and bile
- Tumor may be nodular , miliary or diffuse
- Bursa are always enlarged and may contain nodular tumors
- Tumors are smooth , soft and glistening
- Ecchymotic haemorrhages around skin follicles of wing

fig: diffuse nodular lesions in the liver, spleen and intensine

fig: Diffuse and folicular lesions in the heart
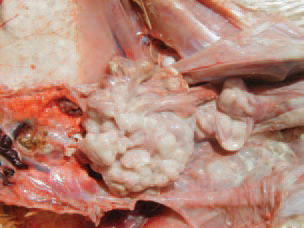
fig: neoplastically transformed ovary in lymphoid leukosis


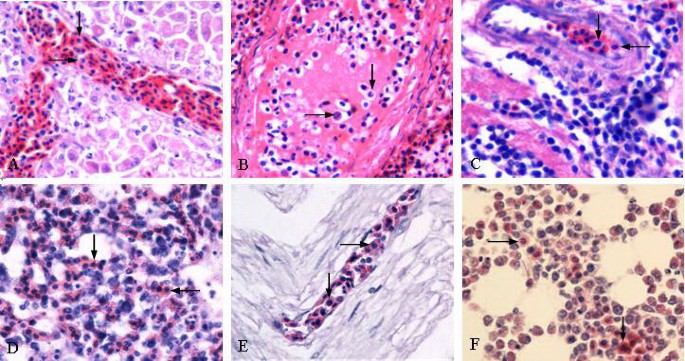
Microscopic lesion :
- Tumor cell looks similar to marek’s disease
- Tumors cells of lymphoid leukosis are larger than normal lymphocytes , have granular chromatin in nucleolus and prominent one or more nucleoli
- On pyronin stain these cells shoe intense rose red ( highly pyroninophilic)
- Interfollicular infiltration of lymphoblast in bursa
- Lymphoid cells are uniform
Diagnosis :
- Signs and symptoms
- PM lesions and tumors are diagnostic
- Virus detection test including PCR, virus isolation
- ELISA kits for detection of antibody
- Tumors can be differentiated from those of Marek’s disease by gross and microscopic pathology and by molecular technique that demonstrate the characteristic clonal integration of proviral DNA into tumor cell growth with the associated disruption of C- myc oncogene
DDX :
- Marek’s disease
- Coligranuloma