AVIAN INFLUENZA
– It is a viral influenza of birds including chickens turkeys and more
- Symptoms vary in severity from asymptomatic infection to mild respiratory and reproductive disease
- Distributed worldwide and are recovered frequently from shorebirds and waterfowl
- Virus may be present in village or backyard flocks
- Young flattening turkeys and laying hens are most affected
ETIOLOGY:
- AI virus are -ve sense ,ss RNA virus in family orthomyxoviridae
- Genius : Influenza A(zoonotic)
- Further classified into : Hemagglutinin (H1- 16|)
Neuraminidase N(1-9) subtypes
TYPES
- Low pathogenicity AI (LPAI) : by H1-4 ,h6 ,h8-10
- Low pathogenicity notifiable AI (LPNAI) : only by h5 and h7
- Highly pathogenicity or highly pathogenic notifiable AI (HPNAI) : only by mutated forms of h5 and h7
TRANSMISSION
- IPis highly variable and ranges from a few days in individual birds to 2 week in flock
Sources of virus
a. Major :
- Infected poultry and live bird markets
- Faces secretion
- Infected water fowl
b. Minor :
- Uncooked infected poultry product h1/h3 swine to tourkeys
- Pet birds
ROUTES OF TRANSMISSION
- Oral ➦ faces / cannibalism
- Aerosol
- Families : people, equipment, vehicles, feed and water, rodents , sparrow , winds , etc
PATHOGENESIS
- Exhibits severe lethargy ,fever Wt loss , transient lymphopenia and replication in upper and lower respiratory tract as well as multiple systemic organs , including brain .
CLINICAL FINDING AND LESIONS
- Clinical sign severity of disease and mortality
rates vary depending on Ai virus strain and host species
- 1. Low pathogenicity AI virus:-
- Respiratory signs as:
- Sneezing coughing
- Ocular and nasal discharge
- Swollen infraorbital sinuses
- Sinusitis is common

- lesions in respiratory tract includes congestion
- In layer and breeders
- Decreased egg production or fertility
- Acute renal failure
- Visceral urate disposition
- Mortality and morbidity is usually low
- high pathogenicity AI virus
- Severe systemic disease with high mortality in chickens

- In peracute cases : lack of sign or grass lesion before death
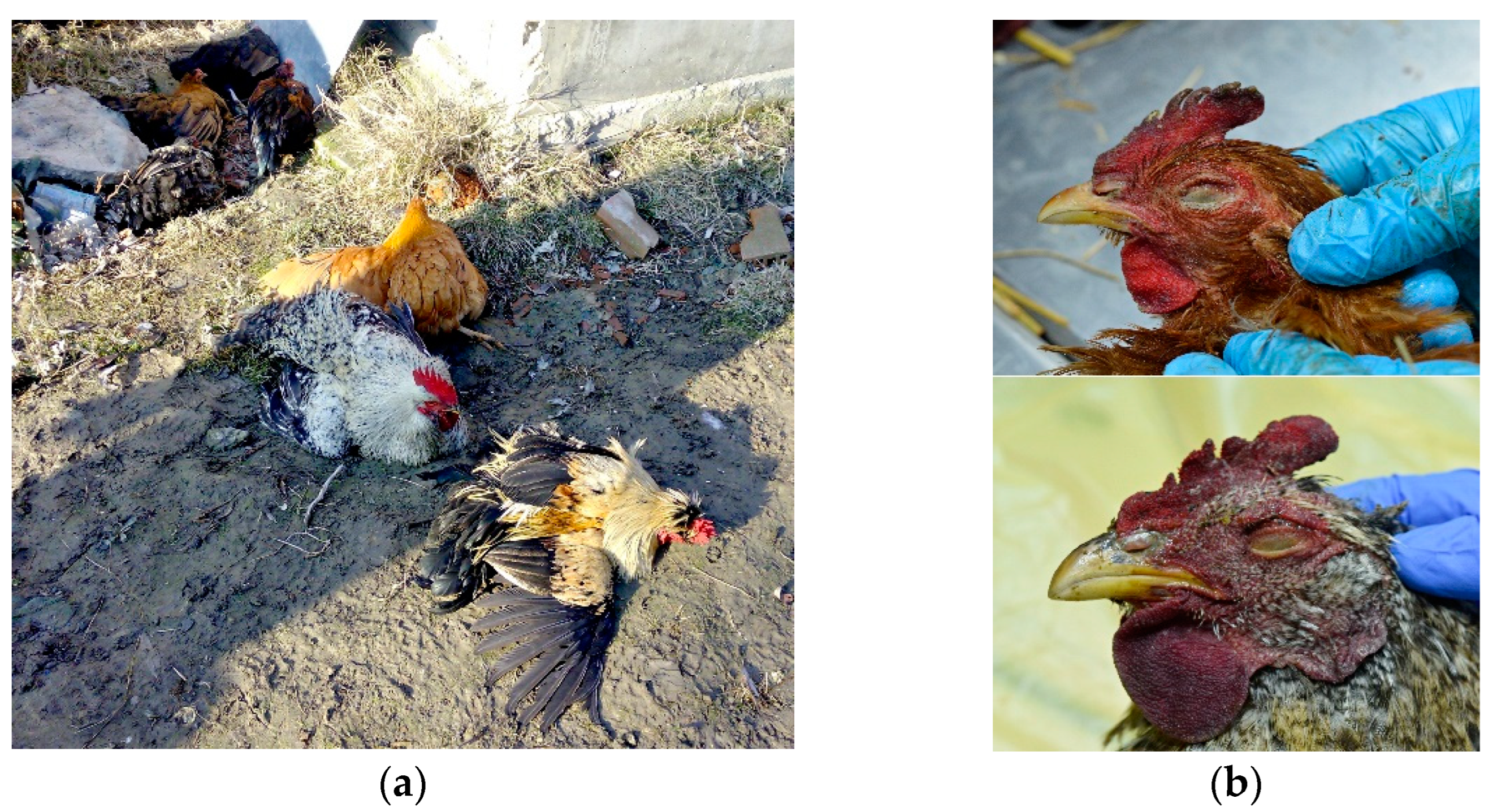
- In acute cases: cyanosis and edema of head, comb and wattle and snood ( turkey)
- Blood-tinged oral and nasal discharges
- Edema and haemorrhages lesions and shanks feed and comb
- In severe cases
– greenish diarrhoea is common
– birds that survive the peracute infection may develop cns involved evident as;
- Torticollis
- Opisthotonus
- incoordination
- paralysis
- drooping wing

Fig :comb and wattle are congested and marked edematous
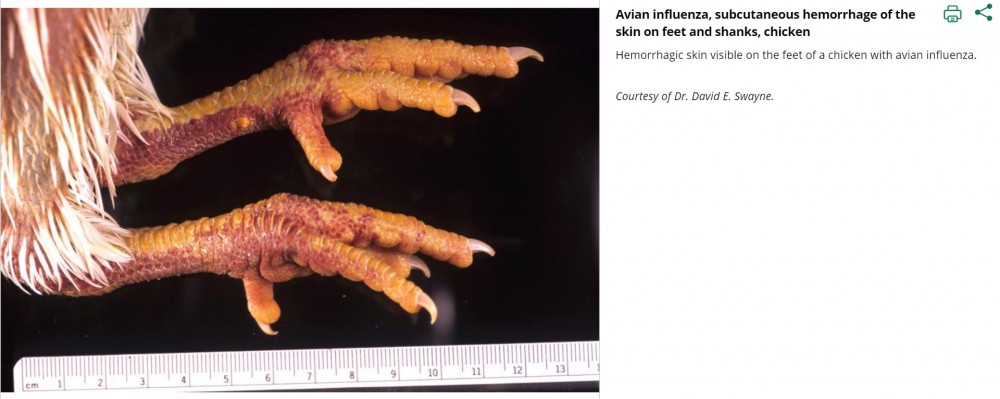
fig : shanks are swollen and extensively haemorrhages
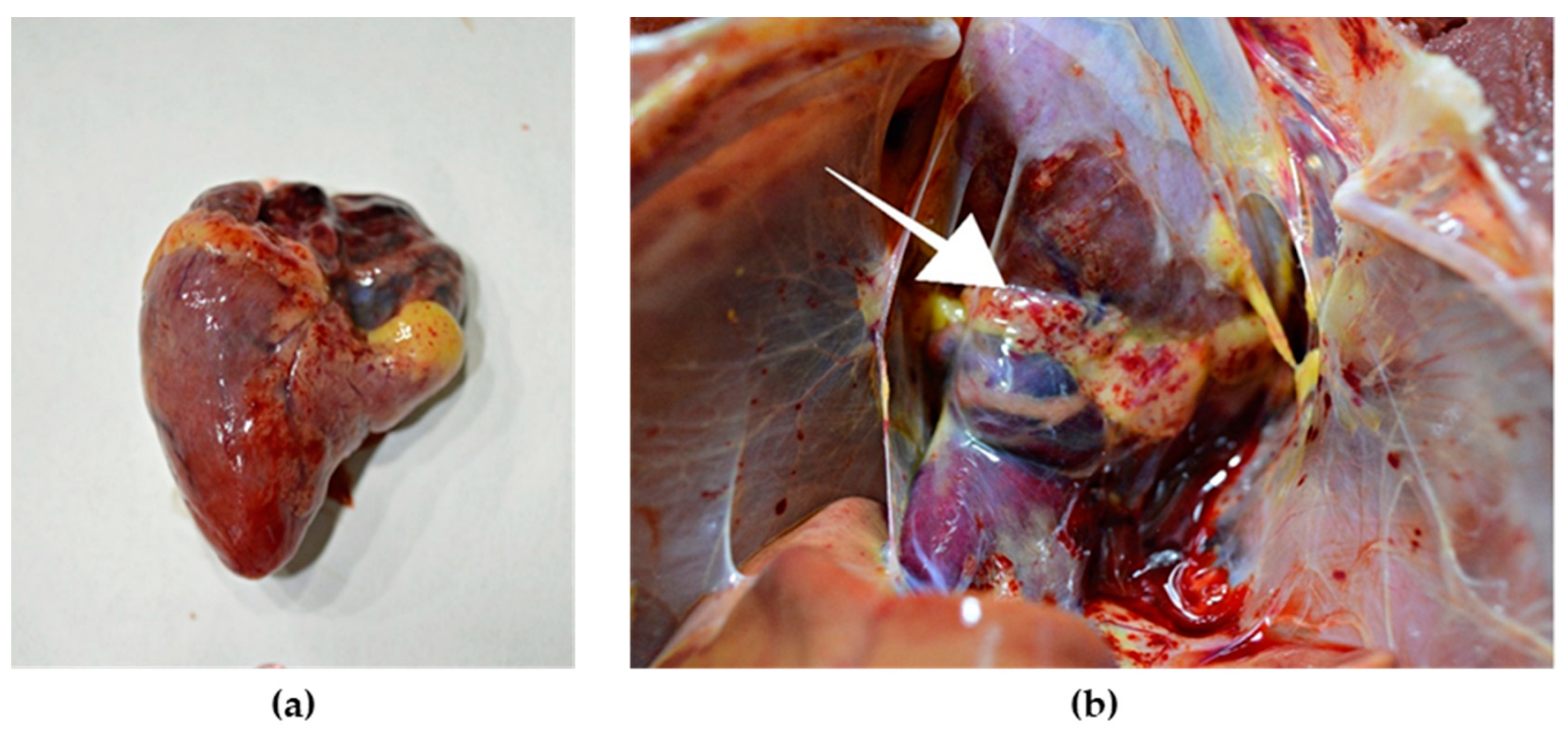
Fig : there are numerous epicardial petechiae

Fig : multiple hemorrhages on mucosal surface of proventriculus

fig : serosal haemorrhages on the Peyer’s patches
MIcroscopic lesions
- Highly variable and may consist of edema , hemorrhage and necrosis in parenchymal cells of multiple visceral organs , skin and CNS
- Subcutaneous ecchymotic hemorrhages : Petechial hemorrhages on visceral organ and in muscles
DIAGNOSIS:-
- LPAI and HPAIvirus can be readily isolated from oropharyngeal and cloacal swabs
AI viruses grow well in the allantoic sac of 9-11 days old embryonated chicken eggs, and they agglutinate RBCs .
- PCR (diagnostic test)
- Detection of AI virus RNA
- Detection of AI specific Antibody
- Serological ( AGID or ELISA )
DDX
1)LPAI :- differentiated from other respiratory disease or causes of decreased egg production including :
- Acute to subacute viral disease ;
- Infectious bronchitis
- Infectious laryngotracheitis
- Low virulent ND
- Infection by other paramyxoviruses
- Bacterial disease ; mycoplasmosis , infectious coryza , fowl cholera (resp. form)
- Fungal disease : aspergillosis
2)HPAI :-
- High mortality such as
- virulent ND
- Peracute septicaemic form of fowl cholera
- Heat exhaustion
- Severe water deprivation