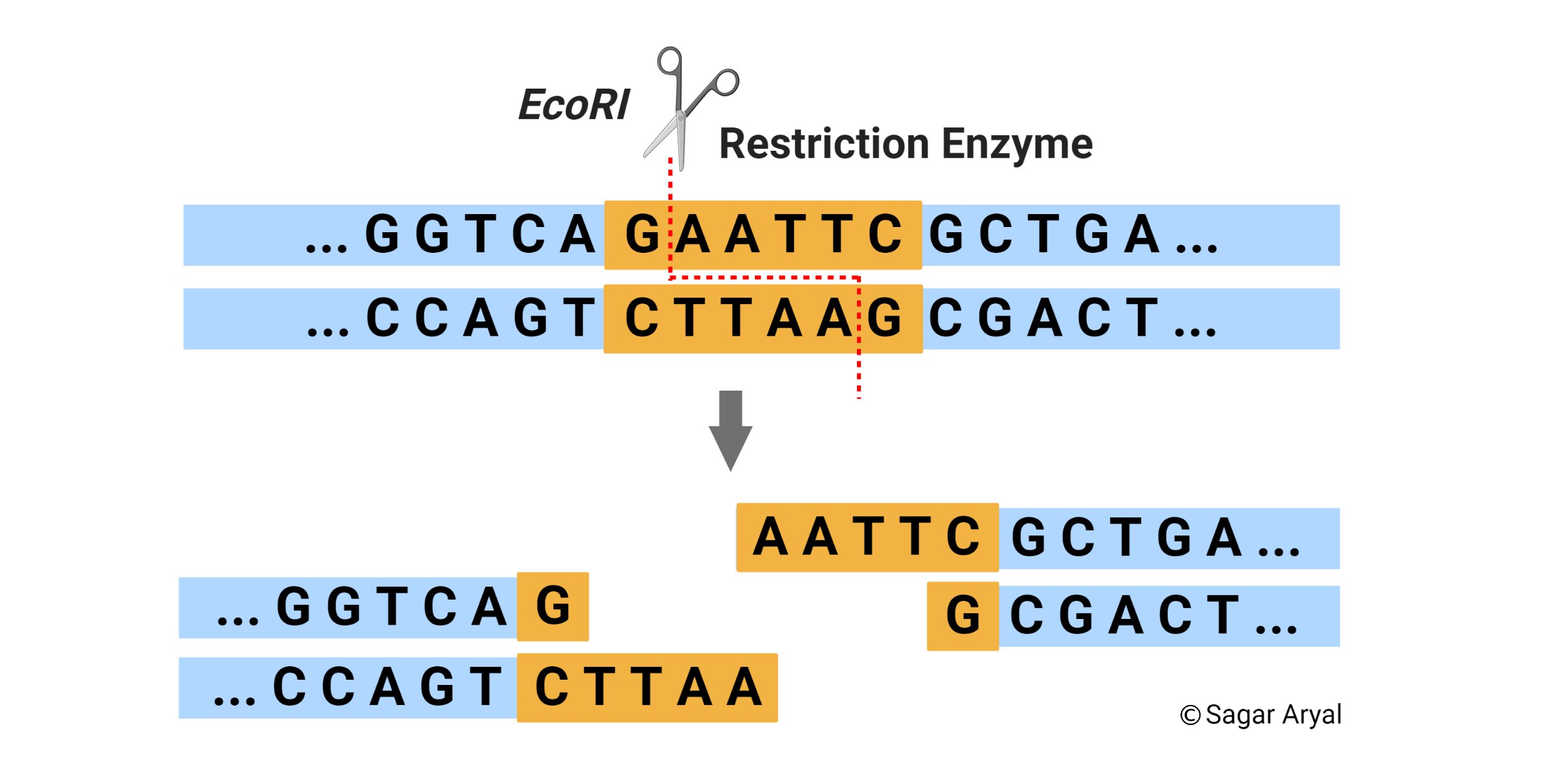
Restriction Enzymes
- Endonucleases are enzymes that produce internal cuts called cleavage in DNA molecules.
- Many endonucleases cleavage DNA molecules at random sites but a class of endonucleases cleaves DNA only within or near those sites which have specific base sequences.
- Such endonucleases are known as restriction endonucleases and the sites recognized by them are called recognition sequences or recognition sites.
- The DNA of a cell is protected from its own endonucleases by methylation within their recognition sites.
- Thus, DNA molecule having the same methylation pattern as that of a bacterial cell itself will be recognized as own DNA while those lacking this will be regarded as foreign DNA.
Types of Restriction Enzymes
a. Type I:
- Cleave DNA about 1000 bp away from 5′ -end of sequence TCA
b. Type II:
- Stable and induce cleavage either within the recognition sequence or very close to them.
c. Type III:
- Intermediate between Type-I and II.
- Cleave DNA in immediate vicinity of their recognition site.
Note: Type I and III are not used in gene cloning.