Immunogenetics
- The immune system of a vertebrate organism provides the body’s main line of defense against invasion by disease causing organisms as bacteria , viruses and fungi.
- The system also attacks cancer cells produced by the organism itself.
- The protein responsible for the immune response in vertebrates are called the antibodies, which are synthesized in response to antigens.
Antibody
- When the body is invaded by a foreign agent whether microbial, a chemical substance, or a larger structure such as dust or a pollen grain, one of the most powerful mechanism for eliminating it is in the production of antibody.
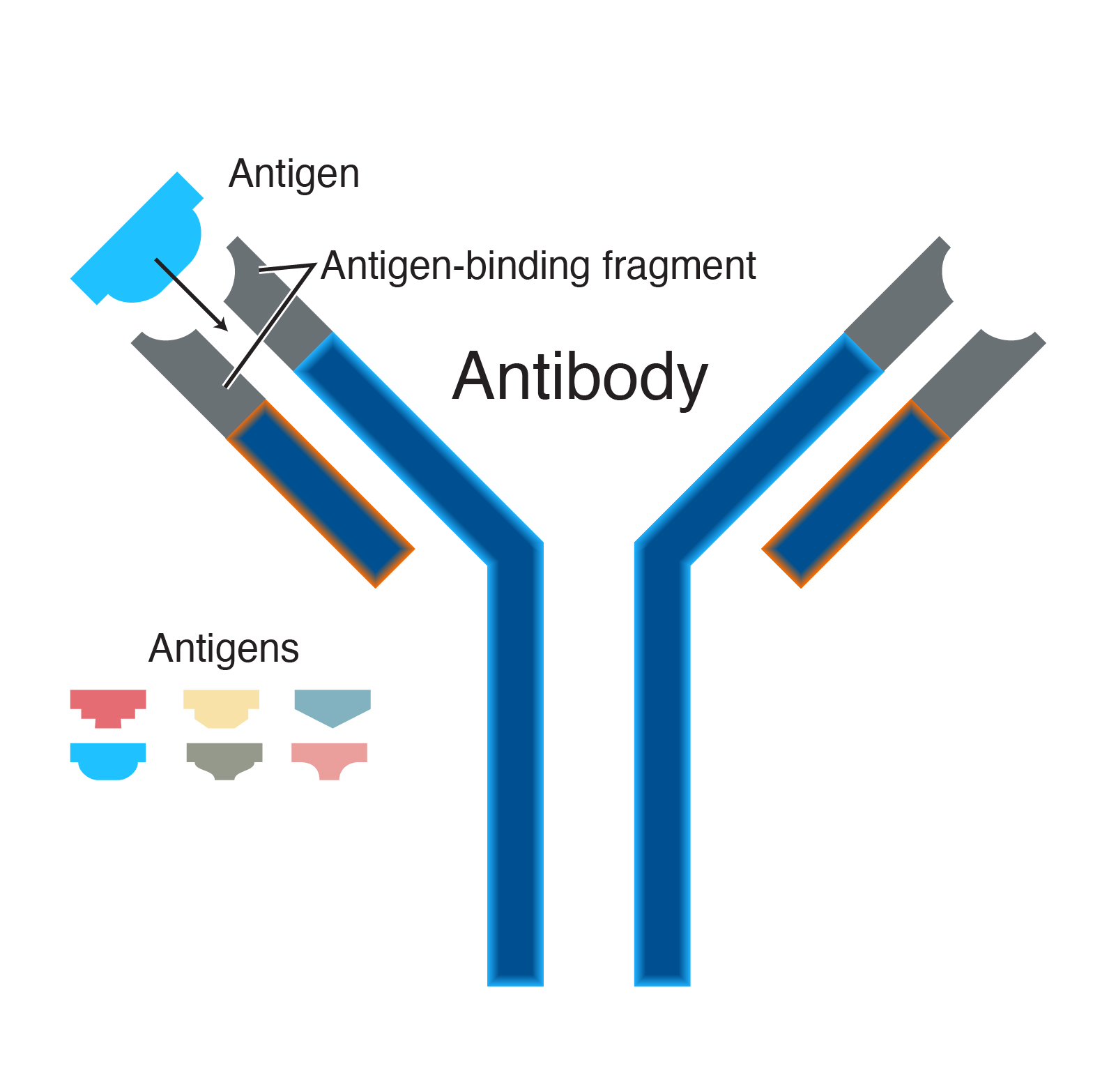
- The antibody is protein that recognizes specific steriochemical shape determined by the invading antigen.
- Each antibody molecule is made up of four immunoglobulin chains.
- There are two identical heavy chains, of 330 or 440 amino acids, and two identical light chains, of 220 amino acids each.
- The four immunoglobulin chains are held together in a form of Y-shaped.
- Virtually all antibody molecules are identical except on the arms of Y.
- This is also where the antigenic specificity of each antibody exists.
- Based on amino acids sequence, it would appear that each polypeptide chain of an antibody is constructed by smaller sub units’ protein called domains.
- The constant proportion of each polypeptide is made of same repeating 110 amino acid domain.
- Each antibody is made up of four polypeptide chains containing larger constant regions of amino acids sequences and small variable regions of amino acid sequence.