Fundamental structure of silicate clay
a. Silicate tetrahedral sheets
- Tetrahedral sheet consist of two planes of oxygen with mainly silicon in the space between the oxygen.
- The basic building block for the tetrahedral sheet is a unit composed of one silicon atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms. It is called the tetrahedronbecause the oxygen define the apices of a four-sided geometric solid that resembles a pyramid (having three ‘sides’ and a base).
- An interlocking array of such tetrahedral, each sharing its basal oxygen with its neighbor, give rise to a tetrahedral sheet.

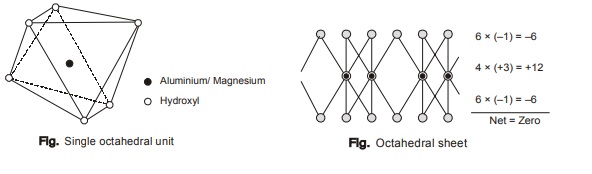
b. Alumina-magnesia octahedral sheets
- Al and/or Mg ions are the key cations in Al-Mg octahedral sheet. Al or Mg ion is surrounded by six O2atoms giving eight sided building blocks termed as octahedron.
- Numerous octahedralinked together horizontally constitute the octahedral sheet. Al dominated sheet is called a dioctahedralsheet and Mg dominated sheet is called a trioctahedralsheet.
- The two Al ions in a dioctahedralsheet satisfy the same negative charge from surrounding O2and OH as three atoms Mg ions in trioctahedralsheet.