Vectors
- A vector, as related to molecular biology, is a DNA molecule (often plasmid or virus) that is used as a vehicle to carry a particular DNA segment into a host cell as part of a cloning or recombinant DNA technique.
Properties of a good vector
- Able to replicate autonomously i.e. independent of the host chromosome replication.
- Should be easy to isolate and purify.
- Should be easily introduced into host cells.
- Should have suitable marker genes that allow easy detection or selection of transformed host cells.
- Should contain unique target sites for as many restriction enzymes as possible.
- Should contain suitable control elements like operator, promoter, ribosome binding site, etc. Such vectors are called expression vector.
Types of vectors
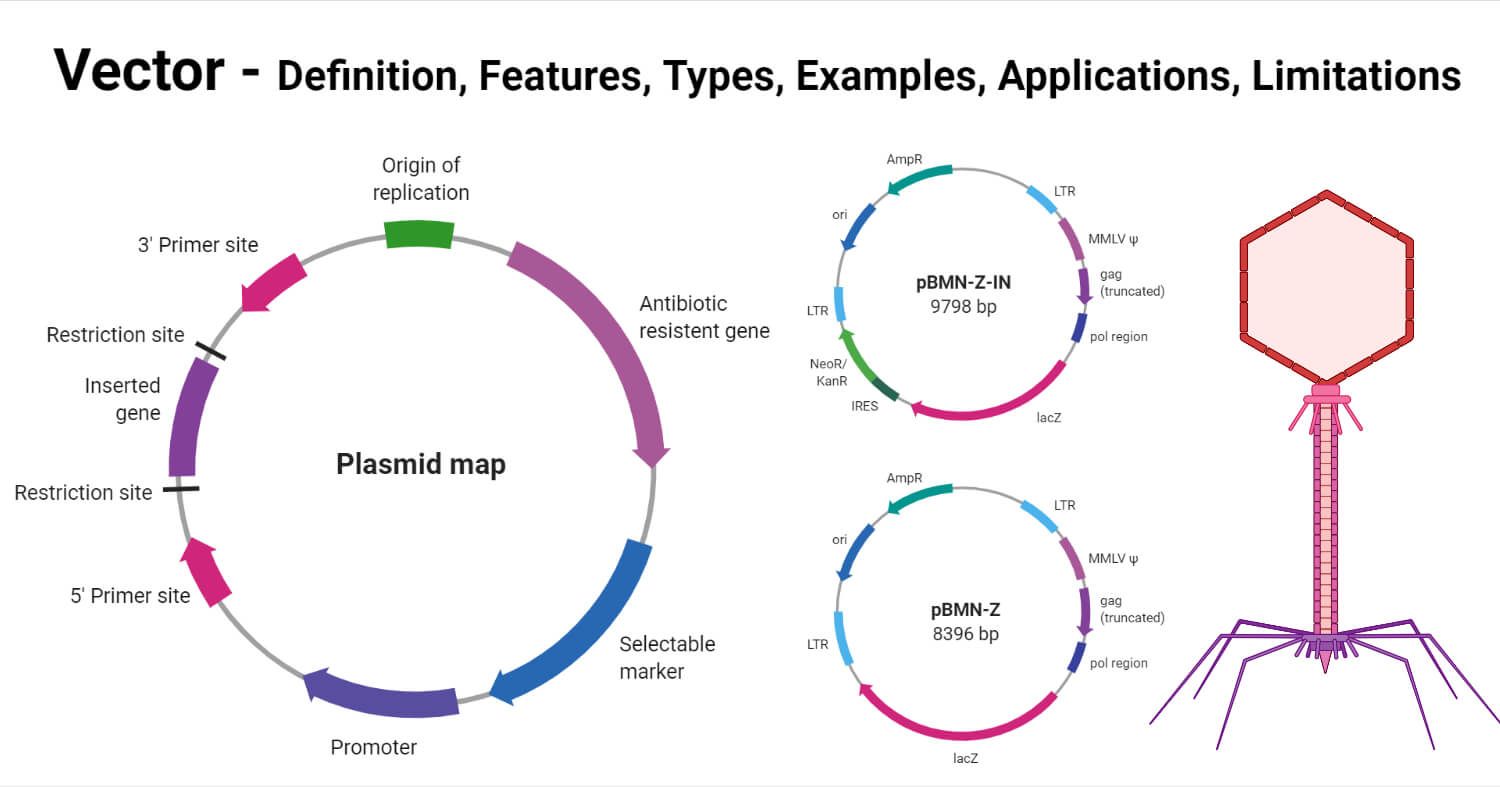
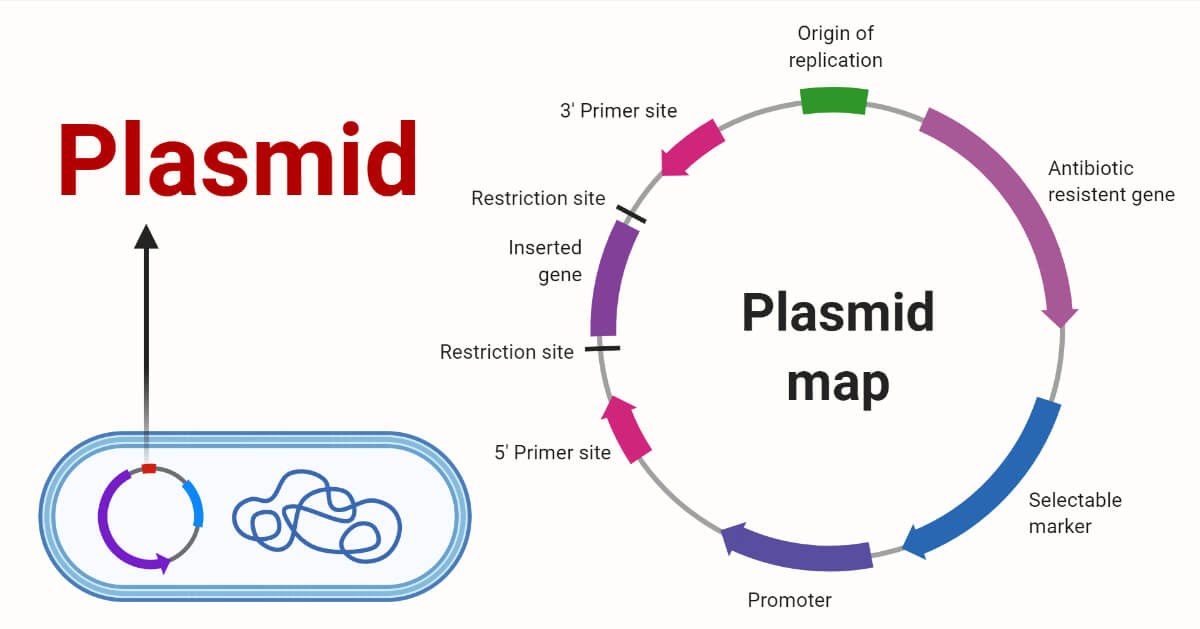
a. Plasmid Vector
- A plasmid is a naturally occurring extra chromosomal double stranded DNA, circular DNA.
- It replicates autonomously within bacterial cell.
- Plasmid carries an origin of replication.
- Plasmid vectors are the simplest cloning vectors.
- It is most widely used for gene cloning.
- Common plasmid vectors are PBR322, PUC, Pi and Ri plasmid.
b. Cosmids Vector
- It is a type of hybrid plasmid.
- It contains lambda phage cos sequence.
- Cosmids = cos sites + plasmid.
- Genomic size of cosmids is about 30 to 52 kb.
- If they have suitable origin of replication than they can replicate as Plasmid within the host cells, E.g.- SV40 Ori, ColE1 ori.
- It also contains selectable marker such as Ampicillin resistance gene.
- Collins and Hohn in 1978 was first to describe cosmids.

c. Phage Vector or Bacteriophage Vector
- Bacteriophages are viruses that attacks bacteria.
- The Phages are simple in structure.
- It consists of DNA molecules having several gene for replication which is surrounded by Capsid.
On the basis of structure bacteria phases are of two types:
I. Head and Tail Phages- E.g.: lambda phage.
ii. Filamentous phage- E.g.: M13 phage.
Lambda Phage Vectors
- Its genome size is about 48,502 bp.
- It contains origin of replication, genes for head and tail protein and enzymes for DNA replication
- It has more than one recognition sequence for almost all the restriction enzymes.
- It should be larger than 38 kb and smaller than 52 kb to packaged into phage particles.

M13 Phage Vectors
- M13 vectors are used to obtain single- stranded copies of cloned DNA.
- It is 6407 nucleotides long.
- It is circular and 6.4kb in size.
- M13 vector only cause infection in F+ and F’ cells.
- It is used to produce several copies of M13 mp series of vectors.
- Example- M13mp8, M13mp9 etc.
.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=493&height=412)
d. Shuttle Vector
- Shuttle vectors are created to replicates in cell of different type of species.
- They contain two origin of replication, in which one is particular for each host species, also those genes required for their replication and not provided by the host cell.
- This type of vectors are developed by recombinant techniques.
